CAZypedia needs your help! We have many unassigned GH, PL, CE, AA, GT, and CBM pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute to CAZypedia. Read more here, and in the 10th anniversary article in Glycobiology.
New to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
*
Consider attending the 15th Carbohydrate Bioengineering Meeting in Ghent, 5-8 May 2024.
Difference between revisions of "Carbohydrate Binding Module Family 46"
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
CBM46 is a Gram-positive bacterial family that comprise around 110 amino acids. The one member of this family characterized to date did not bind to soluble or insoluble polysaccharides as a discrete entity <cite>Wamalwa2006,Venditto2015</cite>. In the context of the full length enzyme, BhCel5B, the CBM46 (BhCBM46) made a significant contribution to binding xyloglucan and β1,3-β1,4-mixed linked glucans. Thus, an inactive form of the catalytic module of BhCel5B (lacks the catalytic nucleophile) did not bind to β1,3-β1,4-mixed linked glucan and had a K<sub>A</sub> for xyloglucan of 10<sup>4</sup> M<sup>-1</sup> , while the inactive full length enzyme (containing both the GH5 catalytic module and the CBM46) had affinities for the two glucans of 10<sup>5</sup> M<sup>-1</sup>and 5 x 10<sup>7</sup> M<sup>-1</sup>, respectively. | CBM46 is a Gram-positive bacterial family that comprise around 110 amino acids. The one member of this family characterized to date did not bind to soluble or insoluble polysaccharides as a discrete entity <cite>Wamalwa2006,Venditto2015</cite>. In the context of the full length enzyme, BhCel5B, the CBM46 (BhCBM46) made a significant contribution to binding xyloglucan and β1,3-β1,4-mixed linked glucans. Thus, an inactive form of the catalytic module of BhCel5B (lacks the catalytic nucleophile) did not bind to β1,3-β1,4-mixed linked glucan and had a K<sub>A</sub> for xyloglucan of 10<sup>4</sup> M<sup>-1</sup> , while the inactive full length enzyme (containing both the GH5 catalytic module and the CBM46) had affinities for the two glucans of 10<sup>5</sup> M<sup>-1</sup>and 5 x 10<sup>7</sup> M<sup>-1</sup>, respectively. | ||
== Structural Features == | == Structural Features == | ||
| − | The crystal structure of BhCBM46 as a discrete entity and in the full length enzyme (''Bacillus halodurans'' GH5 glucanase BhCel5B) was determined. The CBM displays a classic β-sandwich jelly roll fold. The two β-sheets each contain four anti-parallel β-strands. The order of the β-strands in β-sheet 1 and β-sheet 2 are β1, β2, β5, β4 and β3, β6, β7, β8, respectively. A loop connecting the two βsheets, by linking β-strand 3 and 4, provides an extended planar/slightly curved surface containing five aromatic residues. Mutagenesis and conservation of some of these residues suggests that the loop comprises the ligand binding site in BhCBM46, but only in the context of the full length enzyme <cite>Venditto2015</cite>. | + | [[File:CBM46fold.png|thumb|300px|right|'''Figure 1.''' The fold of BhCel5B from ''B. halodurans'' Xyn10A (see [{{PDBlink}}4v2x PDB ID 4v2x]) highlighting the three modules of the enzyme comprising the N-terminal GH5 catalytic module (blue), internal immunoglobulin domain (green) and the C-terminal CBM46]]The crystal structure of BhCBM46 as a discrete entity and in the full length enzyme (''Bacillus halodurans'' GH5 glucanase BhCel5B) was determined. The CBM displays a classic β-sandwich jelly roll fold (Figure 1) <cite>Venditto2015</cite>. The two β-sheets each contain four anti-parallel β-strands. The order of the β-strands in β-sheet 1 and β-sheet 2 are β1, β2, β5, β4 and β3, β6, β7, β8, respectively. A loop connecting the two βsheets, by linking β-strand 3 and 4, provides an extended planar/slightly curved surface containing five aromatic residues. Mutagenesis and conservation of some of these residues suggests that the loop comprises the ligand binding site in BhCBM46, but only in the context of the full length enzyme shown in '''Figure 1''' (see [{{PDBlink}}4v2x PDB ID 4v2x]) <cite>Venditto2015</cite>. |
== Functionalities == | == Functionalities == | ||
All CBM46s are located at the C-terminus of enzymes that contain an N-terminal GH5_4 catalytic module and a central immunoglobulin domain <cite>Wamalwa2006,Venditto2015</cite>. Deleting BhCBM46 from BhCel5B reduced the activity of the enzyme against β1,3-β1,4-mixed linked glucans by ~80-fold, and it was proposed that the kink in the glucan caused by the β1,3-linkage enabled a single chain to interact with both the catalytic module and CBM46 <cite>Venditto2015</cite>. The inability of a CBM to bind its ligand in isolation but contribute to directing substrate into the active site of the enzyme is similar to the role of CBM3c in some GH9 processive cellulases <cite>Sakon1997</cite>. In contrast the same truncated enzyme displayed similar activity to the wild type enzyme against soluble xyloglucan indicating that the linear trajectory of β-1,4-glucan chains would prevent these polymers from occupying both the substrate binding cleft and CBM binding surface. In contrast BhCBM46 had a substantial impact on the capacity of BhCel5B to hydrolyse the xyloglucan in plant cell walls. It was proposed that the CBM, in conjunction with a region of the catalytic module that is distinct from the active site/substrate binding cleft, tethers the enzyme to regions rich in xyloglucan. This enables the substrate binding cleft to readily access xyloglucan chains that are not interacting with the CBM <cite>Venditto2015</cite>. | All CBM46s are located at the C-terminus of enzymes that contain an N-terminal GH5_4 catalytic module and a central immunoglobulin domain <cite>Wamalwa2006,Venditto2015</cite>. Deleting BhCBM46 from BhCel5B reduced the activity of the enzyme against β1,3-β1,4-mixed linked glucans by ~80-fold, and it was proposed that the kink in the glucan caused by the β1,3-linkage enabled a single chain to interact with both the catalytic module and CBM46 <cite>Venditto2015</cite>. The inability of a CBM to bind its ligand in isolation but contribute to directing substrate into the active site of the enzyme is similar to the role of CBM3c in some GH9 processive cellulases <cite>Sakon1997</cite>. In contrast the same truncated enzyme displayed similar activity to the wild type enzyme against soluble xyloglucan indicating that the linear trajectory of β-1,4-glucan chains would prevent these polymers from occupying both the substrate binding cleft and CBM binding surface. In contrast BhCBM46 had a substantial impact on the capacity of BhCel5B to hydrolyse the xyloglucan in plant cell walls. It was proposed that the CBM, in conjunction with a region of the catalytic module that is distinct from the active site/substrate binding cleft, tethers the enzyme to regions rich in xyloglucan. This enables the substrate binding cleft to readily access xyloglucan chains that are not interacting with the CBM <cite>Venditto2015</cite>. | ||
Revision as of 11:30, 30 January 2018
This page is currently under construction. This means that the Responsible Curator has deemed that the page's content is not quite up to CAZypedia's standards for full public consumption. All information should be considered to be under revision and may be subject to major changes.
- Author: ^^^Harry Gilbert^^^
- Responsible Curator: ^^^Elizabeth Ficko-Blean^^^
| CAZy DB link | |
| http://www.cazy.org/CBM46.html |
Ligand specificities
CBM46 is a Gram-positive bacterial family that comprise around 110 amino acids. The one member of this family characterized to date did not bind to soluble or insoluble polysaccharides as a discrete entity [1, 2]. In the context of the full length enzyme, BhCel5B, the CBM46 (BhCBM46) made a significant contribution to binding xyloglucan and β1,3-β1,4-mixed linked glucans. Thus, an inactive form of the catalytic module of BhCel5B (lacks the catalytic nucleophile) did not bind to β1,3-β1,4-mixed linked glucan and had a KA for xyloglucan of 104 M-1 , while the inactive full length enzyme (containing both the GH5 catalytic module and the CBM46) had affinities for the two glucans of 105 M-1and 5 x 107 M-1, respectively.
Structural Features
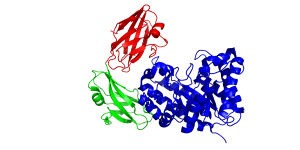
The crystal structure of BhCBM46 as a discrete entity and in the full length enzyme (Bacillus halodurans GH5 glucanase BhCel5B) was determined. The CBM displays a classic β-sandwich jelly roll fold (Figure 1) [2]. The two β-sheets each contain four anti-parallel β-strands. The order of the β-strands in β-sheet 1 and β-sheet 2 are β1, β2, β5, β4 and β3, β6, β7, β8, respectively. A loop connecting the two βsheets, by linking β-strand 3 and 4, provides an extended planar/slightly curved surface containing five aromatic residues. Mutagenesis and conservation of some of these residues suggests that the loop comprises the ligand binding site in BhCBM46, but only in the context of the full length enzyme shown in Figure 1 (see PDB ID 4v2x) [2].
Functionalities
All CBM46s are located at the C-terminus of enzymes that contain an N-terminal GH5_4 catalytic module and a central immunoglobulin domain [1, 2]. Deleting BhCBM46 from BhCel5B reduced the activity of the enzyme against β1,3-β1,4-mixed linked glucans by ~80-fold, and it was proposed that the kink in the glucan caused by the β1,3-linkage enabled a single chain to interact with both the catalytic module and CBM46 [2]. The inability of a CBM to bind its ligand in isolation but contribute to directing substrate into the active site of the enzyme is similar to the role of CBM3c in some GH9 processive cellulases [3]. In contrast the same truncated enzyme displayed similar activity to the wild type enzyme against soluble xyloglucan indicating that the linear trajectory of β-1,4-glucan chains would prevent these polymers from occupying both the substrate binding cleft and CBM binding surface. In contrast BhCBM46 had a substantial impact on the capacity of BhCel5B to hydrolyse the xyloglucan in plant cell walls. It was proposed that the CBM, in conjunction with a region of the catalytic module that is distinct from the active site/substrate binding cleft, tethers the enzyme to regions rich in xyloglucan. This enables the substrate binding cleft to readily access xyloglucan chains that are not interacting with the CBM [2].
Family Firsts
- First Identified
The first CBM46 to be identified (BhCBM46) was from B. halodurans Cel5B [1, 2]
- First Structural Characterization
The first crystal structure of a CBM46 was BhCBM46 [2].
References
- Wamalwa BM, Sakka M, Shiundu PM, Ohmiya K, Kimura T, and Sakka K. (2006). Essentiality of a newly identified carbohydrate-binding module for the function of CelB (BH0603) from the alkaliphilic bacterium Bacillus halodurans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72(10):6851-3. DOI:10.1128/AEM.01209-06 |
- Venditto I, Najmudin S, Luís AS, Ferreira LM, Sakka K, Knox JP, Gilbert HJ, and Fontes CM. (2015). Family 46 Carbohydrate-binding Modules Contribute to the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Xyloglucan and β-1,3-1,4-Glucans through Distinct Mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(17):10572-86. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M115.637827 |
- Sakon J, Irwin D, Wilson DB, and Karplus PA. (1997). Structure and mechanism of endo/exocellulase E4 from Thermomonospora fusca. Nat Struct Biol. 1997;4(10):810-8. DOI:10.1038/nsb1097-810 |