CAZypedia needs your help! We have many unassigned GH, PL, CE, AA, GT, and CBM pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute to CAZypedia. Read more here, and in the 10th anniversary article in Glycobiology.
New to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
*
Consider attending the 15th Carbohydrate Bioengineering Meeting in Ghent, 5-8 May 2024.
Difference between revisions of "Carbohydrate Binding Module Family 67"
m |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== Ligand specificities == | == Ligand specificities == | ||
| − | The sugar binding structure of a [[GH78]] α-ʟ-rhamnosidase from ''Streptomyces avermitilis'' (SaRha78A) revealed a ʟ-rhamnose binding module CBM67 (SaCBM67) within the six-domain arrangement <cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. SaCBM67 bound ʟ-rhamnose and ʟ-mannose with a ''K<sub>a</sub>'' of 7.2 × 10<sup>3</sup> M<sup>−1</sup> and 3.6 × 10<sup>3</sup> M<sup>−1</sup>, and free energy of binding Δ''G'' of −5.3 kcal/mol and −4.8 kcal/mol, respectively, but it did not bind to ʟ-rhamnose in the presence of 5 mM EDTA <cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. Similarly, the D179A and N180A mutants of SaCBM67, in which removed hydrogen bonds with calcium | + | The sugar binding structure of a [[GH78]] α-ʟ-rhamnosidase from ''Streptomyces avermitilis'' (SaRha78A) revealed a ʟ-rhamnose binding module CBM67 (SaCBM67) within the six-domain arrangement <cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. SaCBM67 bound ʟ-rhamnose and ʟ-mannose with a ''K<sub>a</sub>'' of 7.2 × 10<sup>3</sup> M<sup>−1</sup> and 3.6 × 10<sup>3</sup> M<sup>−1</sup>, and free energy of binding Δ''G'' of −5.3 kcal/mol and −4.8 kcal/mol, respectively, but it did not bind to ʟ-rhamnose in the presence of 5 mM EDTA <cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. Similarly, the D179A and N180A mutants of SaCBM67, in which removed hydrogen bonds with calcium abolish ligand binding, confirm the importance of calcium in the binding of SaCBM67 to its ligand <cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. No binding to ʟ-galactose or ʟ-fucose was observed <cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. |
== Structural Features == | == Structural Features == | ||
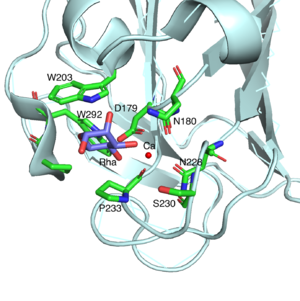
| − | SaCBM67 is a ʟ-rhamnose binding module. The exo binding manner with shallow binding site of SaCBM67 suggests it is a [[Carbohydrate-binding_modules#Types|type C]] CBM. SaRha78A (pdb: 3W5N) forms a multidomain structure comprised of six distinct domains, one α-domain (domain A: catalytic module designated SaRha78<sub>CM</sub>) and five β-domains (domains N, D, E, F, A, and C)<cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. Domain D designated SaCBM67 (P133-P297). SaCBM67 displays weak structural homology with a [[CBM32]], [[CBM35]], [[CBM36]], and [[CBM60]], which recognize their different ligands through either an exo- ([[CBM32]] and [[CBM35]]) or endo-mode ([[CBM36]] and [[CBM60]]) of binding. These CBMs all comprise a β-jellyroll structures and contain a second calcium atom that is integral to ligand recognition (which is absent in CBM32), in addition to a structural calcium (which is absent in CBM67). A central feature of the ʟ-rhamnose binding site in SaCBM67 (Figure 1, see also Fig. 3C of <cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>) is a calcium ion that makes coordinate bonds with O3 and O4 of the sugar. The calcium interacts with SaCBM67 through D179, N180, N228, P233, and a water-mediated contact with S230. The bound ʟ-rhamnose also makes direct hydrogen bonds with W203, N180, and D179 through O2, O3, and O4 atoms, respectively. The C-6 methyl group points toward a small hydrophobic pocket comprising W203, P233, P291 and W292. No direct interaction with the C-6 methyl group explains why SaCBM67 is also capable of binding to ʟ-mannose. | + | SaCBM67 is a ʟ-rhamnose binding module. The exo-binding manner with the shallow binding site of SaCBM67 suggests it is a [[Carbohydrate-binding_modules#Types|type C]] CBM. SaRha78A (pdb: 3W5N) forms a multidomain structure comprised of six distinct domains, one α-domain (domain A: catalytic module designated SaRha78<sub>CM</sub>) and five β-domains (domains N, D, E, F, A, and C)<cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. Domain D is designated as SaCBM67 (P133-P297). SaCBM67 displays weak structural homology with a [[CBM32]], [[CBM35]], [[CBM36]], and [[CBM60]], which recognize their different ligands through either an exo- ([[CBM32]] and [[CBM35]]) or endo-mode ([[CBM36]] and [[CBM60]]) of binding. These CBMs all comprise a β-jellyroll structures and contain a second calcium atom that is integral to ligand recognition (which is absent in CBM32), in addition to a structural calcium (which is absent in CBM67). A central feature of the ʟ-rhamnose binding site in SaCBM67 (Figure 1, see also Fig. 3C of <cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>) is a calcium ion that makes coordinate bonds with O3 and O4 of the sugar. The calcium interacts with SaCBM67 through D179, N180, N228, P233, and a water-mediated contact with S230. The bound ʟ-rhamnose also makes direct hydrogen bonds with W203, N180, and D179 through O2, O3, and O4 atoms, respectively. The C-6 methyl group points toward a small hydrophobic pocket comprising W203, P233, P291 and W292. No direct interaction with the C-6 methyl group explains why SaCBM67 is also capable of binding to ʟ-mannose. |
[[File:SaCBM67_3.png|thumb|300px|right|'''Figure 1.''' The structure of ʟ-rhamnose binding pocket of SaCBM67 [{{PDBlink}}3w5n 3W5N].]] | [[File:SaCBM67_3.png|thumb|300px|right|'''Figure 1.''' The structure of ʟ-rhamnose binding pocket of SaCBM67 [{{PDBlink}}3w5n 3W5N].]] | ||
== Functionalities == | == Functionalities == | ||
| − | + | SaCBM67 shows 2 times higher affinity for ʟ-rhamnose than ʟ-mannose<cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. It binds primarily to ʟ-rhamnose in biological systems because ʟ-mannose seldom exists in natural polysaccharides. The D179A and N180A mutant enzymes lost their binding ability to ʟ-rhamnose which caused a substantial reduction (∼50-fold) in activity against ʟ-rhamnose-containing polysaccharides, these mutations did not influence activity against aryl-rhamnosides <cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. | |
CBM67 members are distributed not only in many bacterial [[GH78]] α-ʟ-rhamnosidases, but also in some Basidiomycete lectins, family 1 pectate lyases, peptidases, and proteins of unknown functions. Protein alignment of candidate members of CBM67 identified five subfamilies within the constructed phylogenetic tree<cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. Although the calcium binding site is conserved in CBM67 members, these CBM67 members might show different sugar specificities because the ʟ-rhamnose binding residues in SaCBM67 are not retained in all the subfamilies. For example, the lectin from ''Pleurotus cornucopiae'', containing two CBM67-like sequences in tandem with sequence identities with SaCBM67 of 25 and 35% for the N- and C-terminal modules, respectively, shows the highest affinity for ''N''-acetyl-ᴅ-galactosamine<cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. | CBM67 members are distributed not only in many bacterial [[GH78]] α-ʟ-rhamnosidases, but also in some Basidiomycete lectins, family 1 pectate lyases, peptidases, and proteins of unknown functions. Protein alignment of candidate members of CBM67 identified five subfamilies within the constructed phylogenetic tree<cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. Although the calcium binding site is conserved in CBM67 members, these CBM67 members might show different sugar specificities because the ʟ-rhamnose binding residues in SaCBM67 are not retained in all the subfamilies. For example, the lectin from ''Pleurotus cornucopiae'', containing two CBM67-like sequences in tandem with sequence identities with SaCBM67 of 25 and 35% for the N- and C-terminal modules, respectively, shows the highest affinity for ''N''-acetyl-ᴅ-galactosamine<cite>Fujimoto2013</cite>. | ||
Revision as of 02:36, 16 November 2018
This page is currently under construction. This means that the Responsible Curator has deemed that the page's content is not quite up to CAZypedia's standards for full public consumption. All information should be considered to be under revision and may be subject to major changes.
- Author: ^^^Satoshi Kaneko^^^
- Responsible Curator: ^^^Harry Gilbert^^^
| CAZy DB link | |
| http://www.cazy.org/CBM67.html |
Ligand specificities
The sugar binding structure of a GH78 α-ʟ-rhamnosidase from Streptomyces avermitilis (SaRha78A) revealed a ʟ-rhamnose binding module CBM67 (SaCBM67) within the six-domain arrangement [1]. SaCBM67 bound ʟ-rhamnose and ʟ-mannose with a Ka of 7.2 × 103 M−1 and 3.6 × 103 M−1, and free energy of binding ΔG of −5.3 kcal/mol and −4.8 kcal/mol, respectively, but it did not bind to ʟ-rhamnose in the presence of 5 mM EDTA [1]. Similarly, the D179A and N180A mutants of SaCBM67, in which removed hydrogen bonds with calcium abolish ligand binding, confirm the importance of calcium in the binding of SaCBM67 to its ligand [1]. No binding to ʟ-galactose or ʟ-fucose was observed [1].
Structural Features
SaCBM67 is a ʟ-rhamnose binding module. The exo-binding manner with the shallow binding site of SaCBM67 suggests it is a type C CBM. SaRha78A (pdb: 3W5N) forms a multidomain structure comprised of six distinct domains, one α-domain (domain A: catalytic module designated SaRha78CM) and five β-domains (domains N, D, E, F, A, and C)[1]. Domain D is designated as SaCBM67 (P133-P297). SaCBM67 displays weak structural homology with a CBM32, CBM35, CBM36, and CBM60, which recognize their different ligands through either an exo- (CBM32 and CBM35) or endo-mode (CBM36 and CBM60) of binding. These CBMs all comprise a β-jellyroll structures and contain a second calcium atom that is integral to ligand recognition (which is absent in CBM32), in addition to a structural calcium (which is absent in CBM67). A central feature of the ʟ-rhamnose binding site in SaCBM67 (Figure 1, see also Fig. 3C of [1]) is a calcium ion that makes coordinate bonds with O3 and O4 of the sugar. The calcium interacts with SaCBM67 through D179, N180, N228, P233, and a water-mediated contact with S230. The bound ʟ-rhamnose also makes direct hydrogen bonds with W203, N180, and D179 through O2, O3, and O4 atoms, respectively. The C-6 methyl group points toward a small hydrophobic pocket comprising W203, P233, P291 and W292. No direct interaction with the C-6 methyl group explains why SaCBM67 is also capable of binding to ʟ-mannose.
Functionalities
SaCBM67 shows 2 times higher affinity for ʟ-rhamnose than ʟ-mannose[1]. It binds primarily to ʟ-rhamnose in biological systems because ʟ-mannose seldom exists in natural polysaccharides. The D179A and N180A mutant enzymes lost their binding ability to ʟ-rhamnose which caused a substantial reduction (∼50-fold) in activity against ʟ-rhamnose-containing polysaccharides, these mutations did not influence activity against aryl-rhamnosides [1].
CBM67 members are distributed not only in many bacterial GH78 α-ʟ-rhamnosidases, but also in some Basidiomycete lectins, family 1 pectate lyases, peptidases, and proteins of unknown functions. Protein alignment of candidate members of CBM67 identified five subfamilies within the constructed phylogenetic tree[1]. Although the calcium binding site is conserved in CBM67 members, these CBM67 members might show different sugar specificities because the ʟ-rhamnose binding residues in SaCBM67 are not retained in all the subfamilies. For example, the lectin from Pleurotus cornucopiae, containing two CBM67-like sequences in tandem with sequence identities with SaCBM67 of 25 and 35% for the N- and C-terminal modules, respectively, shows the highest affinity for N-acetyl-ᴅ-galactosamine[1].
Family Firsts
- First Identified
- SaCBM67 from the S. avermitilis α-ʟ-rhamnosidase SaRha78A was the first member of the family to be identified and characterized [1].
- First Structural Characterization
- The first structure of CBM67 is a module involved in BsRhaB from Bacillus sp. GL1 [2], but the function of the module has not been demonstrated. The first structure-based characterization of a characterized member of CBM67 was SaCBM67 [1].
References
- Fujimoto Z, Jackson A, Michikawa M, Maehara T, Momma M, Henrissat B, Gilbert HJ, and Kaneko S. (2013). The structure of a Streptomyces avermitilis α-L-rhamnosidase reveals a novel carbohydrate-binding module CBM67 within the six-domain arrangement. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(17):12376-85. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M113.460097 |
- Cui Z, Maruyama Y, Mikami B, Hashimoto W, and Murata K. (2007). Crystal structure of glycoside hydrolase family 78 alpha-L-Rhamnosidase from Bacillus sp. GL1. J Mol Biol. 2007;374(2):384-98. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.09.003 |