CAZypedia needs your help! We have many unassigned GH, PL, CE, AA, GT, and CBM pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute to CAZypedia. Read more here, and in the 10th anniversary article in Glycobiology.
New to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
*
Consider attending the 15th Carbohydrate Bioengineering Meeting in Ghent, 5-8 May 2024.
Glycoside Hydrolase Family 164
This page is currently under construction. This means that the Responsible Curator has deemed that the page's content is not quite up to CAZypedia's standards for full public consumption. All information should be considered to be under revision and may be subject to major changes.
- Author: ^^^Zachary Armstrong^^^
- Responsible Curator: ^^^Gideon Davies^^^
| Glycoside Hydrolase Family GH164 | |
| Clan | GH-x |
| Mechanism | retaining/inverting |
| Active site residues | known/not known |
| CAZy DB link | |
| http://www.cazy.org/GH164.html | |
Substrate specificities
Content is to be added here.
Kinetics and Mechanism
Content is to be added here.
Catalytic Residues
Content is to be added here.
Three-dimensional structures
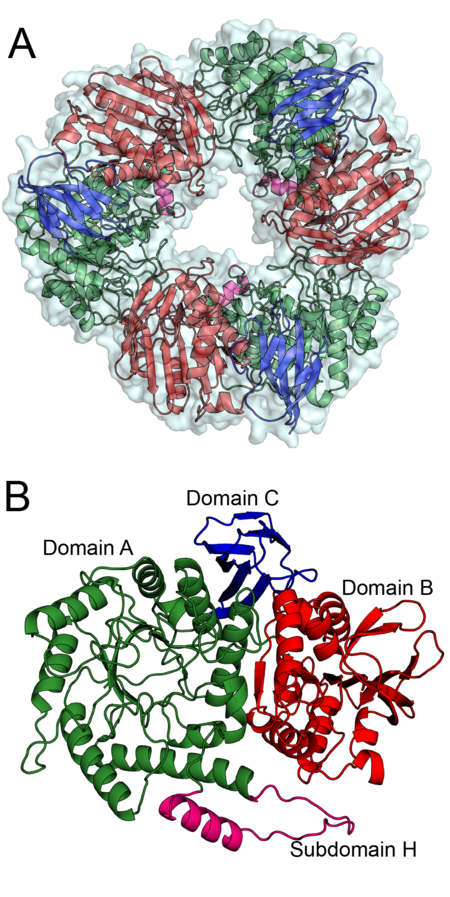
To date only the structure of Bacteroidetes salyersiae β-mannosidase (Bs164) has been solved. Bs164 exists as a donut shaped trimer, see figure 1A. Each trimer-donut has an outer diameter of approximately 100 Å and an internal diameter of between 30 and 35 Å. The individual Bs164 chains contain three clearly defined domains: a modified (β/α)8 barrel, a domain containing a seven membered mixed β-sheet sandwiched between α-helices, and a β-sheet domain (Figure 1B). This domain architecture is quite similar to that seen for family GH42 enzymes [1], but is previously unseen for β-mannosidases.
Family Firsts
- First sterochemistry determination
- Bacteroides salyersiae β-mannosidase by NMR [2]
- First catalytic nucleophile identification
- Bacteroides salyersiae β-mannosidase by 2-fluoromannose labeling and kinetic analysis of mutants [2]
- First general acid/base residue identification
- Bacteroides salyersiae β-mannosidase by kinetic analysis of mutants [2]
- First 3-D structure of a GH1 enzyme
- Bacteroides salyersiae β-mannosidase [2]
References
- Hidaka M, Fushinobu S, Ohtsu N, Motoshima H, Matsuzawa H, Shoun H, and Wakagi T. (2002). Trimeric crystal structure of the glycoside hydrolase family 42 beta-galactosidase from Thermus thermophilus A4 and the structure of its complex with galactose. J Mol Biol. 2002;322(1):79-91. DOI:10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00746-5 |
- Armstrong Z and Davies GJ. (2020). Structure and function of Bs164 β-mannosidase from Bacteroides salyersiae the founding member of glycoside hydrolase family GH164. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(13):4316-4326. DOI:10.1074/jbc.RA119.011591 |