CAZypedia celebrates the life of Senior Curator Emeritus Harry Gilbert, a true giant in the field, who passed away in September 2025.
CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article. Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Difference between revisions of "Carbohydrate Binding Module Family 20"
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
:The first CBM20 was recognised in the early 1980s at the C-termini of glucoamylases from <i>A. awamori</i> <cite>Hayashida1982</cite> and <i>A. niger</i> <cite>Svensson1982 Svensson1983 Boel1984</cite>. | :The first CBM20 was recognised in the early 1980s at the C-termini of glucoamylases from <i>A. awamori</i> <cite>Hayashida1982</cite> and <i>A. niger</i> <cite>Svensson1982 Svensson1983 Boel1984</cite>. | ||
;First Structural Characterization | ;First Structural Characterization | ||
| − | :The first structure of CBM20 was the structure of a [[GH13]] CGTase from <i>Bacillus circulans</i> (PDB entry [{{PDBlink}}1cgt 1CGT]) <cite>Klein1991</cite>. The first CBM20 structure with a ligand bound was the | + | :The first structure of CBM20 was the structure of a [[GH13]] CGTase from <i>Bacillus circulans</i> 8 (PDB entry [{{PDBlink}}1cgt 1CGT]) <cite>Klein1991</cite>. The first CBM20 structure with a ligand bound was the structure of the [[GH13]] CGTase from <i>Bacillus circulans</i> 251 (PDB entry [{{PDBlink}}1cdg 1CDG]) <cite>Lawson1994</cite>. |
<!-- :Insert archetype here, possibly including ''very brief'' synopsis. --> | <!-- :Insert archetype here, possibly including ''very brief'' synopsis. --> | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
#Klein1991 pmid=1826034 | #Klein1991 pmid=1826034 | ||
| + | #Lawson1994 pmid=8107143 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
[[Category:Carbohydrate Binding Module Families|CBM020]] | [[Category:Carbohydrate Binding Module Families|CBM020]] | ||
Revision as of 11:23, 15 December 2019
This page is currently under construction. This means that the Responsible Curator has deemed that the page's content is not quite up to CAZypedia's standards for full public consumption. All information should be considered to be under revision and may be subject to major changes.
- Author: ^^^Marie Sofie Møller^^^
- Responsible Curators: ^^^Birte Svensson^^^ and ^^^Stephan Janecek^^^
| CAZy DB link | |
| https://www.cazy.org/CBM20.html |
Ligand specificities
CBM20 modules bind starch granules (raw starch), its soluble components amylose and amylopectin as well as derived maltooligosaccharides (maltose, maltoheptaose, maltodecaose). Furthermore ɑ-, β-, and γ-cyclodextrin, which mimic amylose, have been used for studying CBM20-carbohydrate binding.
Structural Features
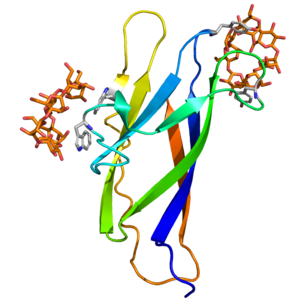
The CBM20 members are type B CBMs and their overall fold is a β-sandwich (Fig. 1). At least one but more typically two binding sites have been found in determined structures having the CBM20 complexed with bound carbohydrate. Such complexes have been studied for modules originating from several amylolytic enzymes, e.g. GH13_2 cyclodextrin glucanotransferase (CGTase) from Bacillus circulans [2], GH14 β-amylase from Bacillus cereus [3] and GH15 glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger [1], as well as the human glucan phosphatase laforin [4]. The two binding sites of CBM20 have been best illustrated in the NMR structure of the isolated module from A. niger glucoamylase complexed with β-cyclodextrin (Fig. 1) [1] and the X-ray structure of the module of the intact B. circulans CGTase in complex with maltose [2]. Binding site 1, important for raw starch binding ability, is formed from two tryptophan residues (Trp543 and Trp590 in the glucoamylase and Trp616 and Trp662 in the CGTase) making a compact and rigid hydrophobic site exposed on the surface and well adapted to bind glucose residues in the cyclodextrin ligands, considered as starch mimics. This small and easily accessible site may function as the place where the starch is initially recognized and it in fact does not change conformation after β-cyclodextrin binding compared to the free CBM20 [5]. It is worth mentioning that both tryptophan residues make stacking interactions with glucose rings and are conserved in the sequence alignment of CBM20s [6]. This is not the case, however, for aromatic residues stacked against glucose rings in binding site 2, which may function to guide the starch chains to the active site and is thus more extended and flexible, undergoing a larger conformational rearrangement when binding the β-cyclodextrin [1]. While there are two tyrosines (Tyr527 and Tyr556) in the glucoamylase binding site 2, only one aromatic residue (Tyr633, corresponding to the Tyr556) is believed to play the analogous role in the CGTase. On the other hand, a third well-conserved tryptophan residue (Trp563 in glucoamylase and Trp636 in CGTase), although buried and thus not able to interact with β-cyclodextrin directly, was found to be involved in making contacts with several residues at binding site 2 [1].
Functionalities
The CBM20 from the A. niger glucoamylase has been shown not only to bind starch but also disrupting its surface, thereby enhancing the amylolytic rate [7]. A CBM20 from an auxiliary activities family AA13 starch polysaccharide monooxygenase was shown to be important for amylose binding and activity on amylose [8]. The enzymes, of which the CBM20 module constitutes a domain, have predominantly specificities from the ɑ-amylase family GH13 or enzymes from GH77, but can also belong to GH14 β-amylases and GH15 glucoamylases [9]. Among other CAZy GH families, the CBM20 is in some cases found associated with enzymes from GH31, GH57, GH119 and the auxiliary activities family AA13. Furthermore, CBM20 modules have been recognised in enzymes of which the catalytic domain is not classified in CAZy. Examples are phosphoglucan, water dikinase, glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase-5, laforin, and genethonin-1 [6]. The modules of family CBM20 have commonly been found in a single copy and usually appear without SBDs from other CBM families within the same protein, although co-occurence has been observed with CBM25, CBM34, and CBM48 [6].
Family Firsts
- First Identified
- The first CBM20 was recognised in the early 1980s at the C-termini of glucoamylases from A. awamori [10] and A. niger [11, 12, 13].
- First Structural Characterization
- The first structure of CBM20 was the structure of a GH13 CGTase from Bacillus circulans 8 (PDB entry 1CGT) [14]. The first CBM20 structure with a ligand bound was the structure of the GH13 CGTase from Bacillus circulans 251 (PDB entry 1CDG) [15].
References
- Sorimachi K, Le Gal-Coëffet MF, Williamson G, Archer DB, and Williamson MP. (1997). Solution structure of the granular starch binding domain of Aspergillus niger glucoamylase bound to beta-cyclodextrin. Structure. 1997;5(5):647-61. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00220-7 |
- Penninga D, van der Veen BA, Knegtel RM, van Hijum SA, Rozeboom HJ, Kalk KH, Dijkstra BW, and Dijkhuizen L. (1996). The raw starch binding domain of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from Bacillus circulans strain 251. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(51):32777-84. DOI:10.1074/jbc.271.51.32777 |
- Mikami B, Adachi M, Kage T, Sarikaya E, Nanmori T, Shinke R, and Utsumi S. (1999). Structure of raw starch-digesting Bacillus cereus beta-amylase complexed with maltose. Biochemistry. 1999;38(22):7050-61. DOI:10.1021/bi9829377 |
- Raththagala M, Brewer MK, Parker MW, Sherwood AR, Wong BK, Hsu S, Bridges TM, Paasch BC, Hellman LM, Husodo S, Meekins DA, Taylor AO, Turner BD, Auger KD, Dukhande VV, Chakravarthy S, Sanz P, Woods VL Jr, Li S, Vander Kooi CW, and Gentry MS. (2015). Structural mechanism of laforin function in glycogen dephosphorylation and lafora disease. Mol Cell. 2015;57(2):261-72. DOI:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.11.020 |
- Sorimachi K, Jacks AJ, Le Gal-Coëffet MF, Williamson G, Archer DB, and Williamson MP. (1996). Solution structure of the granular starch binding domain of glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1996;259(5):970-87. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0374 |
- Janeček Š, Mareček F, MacGregor EA, and Svensson B. (2019). Starch-binding domains as CBM families-history, occurrence, structure, function and evolution. Biotechnol Adv. 2019;37(8):107451. DOI:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107451 |
- Southall SM, Simpson PJ, Gilbert HJ, Williamson G, and Williamson MP. (1999). The starch-binding domain from glucoamylase disrupts the structure of starch. FEBS Lett. 1999;447(1):58-60. DOI:10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00263-x |
- Vu VV, Hangasky JA, Detomasi TC, Henry SJW, Ngo ST, Span EA, and Marletta MA. (2019). Substrate selectivity in starch polysaccharide monooxygenases. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(32):12157-12166. DOI:10.1074/jbc.RA119.009509 |
- Janeček Š, Svensson B, and MacGregor EA. (2011). Structural and evolutionary aspects of two families of non-catalytic domains present in starch and glycogen binding proteins from microbes, plants and animals. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2011;49(5):429-40. DOI:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2011.07.002 |
-
Hayashida, S., Kunisaki, S., Nakao, M. and Flor, P.Q. (1982) Evidence for raw starch-affinity site on Aspergillus awamori glucoamylase I. Agric. Biol. Chem., vol. 46, pp. 83-89.
-
Svensson, B., Pedersen, T.G., Svendsen, I., Sakai, T. and Ottesen, M. (1982) Characterization of two forms of glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger. Carlsb. Res. Commun. vol. 47, pp. 55-69.
-
Svensson, B., Larsen, K., Svendsen, I., and Boel, E. (1983) The complete amino acid sequence of the glycoprotein, glucoamylase G1, from Aspergillus niger. Carlsb. Res. Commun. vol. 48, pp. 529-544.
- Boel E, Hjort I, Svensson B, Norris F, Norris KE, and Fiil NP. (1984). Glucoamylases G1 and G2 from Aspergillus niger are synthesized from two different but closely related mRNAs. EMBO J. 1984;3(5):1097-102. DOI:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01935.x |
- Klein C and Schulz GE. (1991). Structure of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase refined at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991;217(4):737-50. DOI:10.1016/0022-2836(91)90530-j |
- Lawson CL, van Montfort R, Strokopytov B, Rozeboom HJ, Kalk KH, de Vries GE, Penninga D, Dijkhuizen L, and Dijkstra BW. (1994). Nucleotide sequence and X-ray structure of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from Bacillus circulans strain 251 in a maltose-dependent crystal form. J Mol Biol. 1994;236(2):590-600. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1994.1168 |