CAZypedia celebrates the life of Senior Curator Emeritus Harry Gilbert, a true giant in the field, who passed away in September 2025.
CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article. Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Difference between revisions of "Carbohydrate Binding Module Family 91"
Daichi Ito (talk | contribs) |
Daichi Ito (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
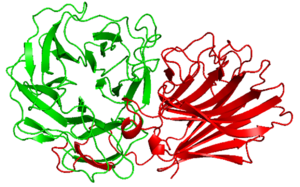
Alpha Fold 2 structure analysis of ''Px''CBM91 exhibited a β-sandwich fold consisted of 12 β-strands curving in the one direction. The concave and loops around it connecting each β-strands possesses several hydrophobic amino acid residues and the surface would be the binding site. | Alpha Fold 2 structure analysis of ''Px''CBM91 exhibited a β-sandwich fold consisted of 12 β-strands curving in the one direction. The concave and loops around it connecting each β-strands possesses several hydrophobic amino acid residues and the surface would be the binding site. | ||
== Functionalities == | == Functionalities == | ||
| − | CBM91 often is | + | CBM91 often is connected to the β-xylosidases belonging to glycoside hydrolase family 43, for example. CBM91 binds to the substrates and would places the catalytic domain at the vicinity of substrates in which substrate concentration is high. These emzymes would utilize CBM91 as a tool for efficient saccharification by combination with other xylanases which release xylobiose and/or xylo-oligosaccharides from insoluble substrates. |
Revision as of 06:08, 23 April 2024
This page is currently under construction. This means that the Responsible Curator has deemed that the page's content is not quite up to CAZypedia's standards for full public consumption. All information should be considered to be under revision and may be subject to major changes.
| CAZy DB link | |
| https://www.cazy.org/CBM91.html |
Ligand specificities
CBM91 bound to oat spelt xylan with Ka value of 2.0×10-5 M-1, and bind birchwood xylan. But it does not bind to cellulosic substrates (carboxymethyl-cellulose, ball-milled cellulose and lichnan). So, CBM91 can recognize and bind to insoluble xylan [1].
Structural Features
Alpha Fold 2 structure analysis of PxCBM91 exhibited a β-sandwich fold consisted of 12 β-strands curving in the one direction. The concave and loops around it connecting each β-strands possesses several hydrophobic amino acid residues and the surface would be the binding site.
Functionalities
CBM91 often is connected to the β-xylosidases belonging to glycoside hydrolase family 43, for example. CBM91 binds to the substrates and would places the catalytic domain at the vicinity of substrates in which substrate concentration is high. These emzymes would utilize CBM91 as a tool for efficient saccharification by combination with other xylanases which release xylobiose and/or xylo-oligosaccharides from insoluble substrates.
Family Firsts
- First Identified
- PxCBM91 from Paenibacillus xynaniclasticus strain TW1 [1].
- First Structural Characterization
- β-D-xylosidase, a family 43 glycoside hydrolase from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 PDB ID 1Y7B.
References
- Ito D, Nakano E, Karita S, Umekawa M, Ratanakhanokchai K, and Tachaapaikoon C. (2022). Characterization of a GH Family 43 β-Xylosidase Having a Novel Carbohydrate-binding Module from Paenibacillus xylaniclasticus Strain TW1. J Appl Glycosci (1999). 2022;69(3):65-71. DOI:10.5458/jag.jag.JAG-2022_0001 |