CAZypedia needs your help! We have many unassigned GH, PL, CE, AA, GT, and CBM pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute to CAZypedia. Read more here, and in the 10th anniversary article in Glycobiology.
New to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
*
Consider attending the 15th Carbohydrate Bioengineering Meeting in Ghent, 5-8 May 2024.
Difference between revisions of "Glycoside Hydrolase Family 136"
Harry Brumer (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "\^\^\^(.*)\^\^\^" to "$1") |
(Mechanism and family firsts) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
== Substrate specificities == | == Substrate specificities == | ||
| − | This family of glycoside hydrolases contains lacto-''N''-biosidase, as demonstrated for LnbX from ''Bifidobacterium longum'' JCM 1217 <cite>Sakurama2013</cite>. LnbX liberates Galβ1-3GlcNAc(lacto-''N''-biose I, LNB) and lactose from lacto-''N''-tetraose, the main component of human milk oligosaccharides. It hydrolyzed the linkage GlcNAcβ1-3Gal in lacto-''N''-hexaose, lacto-''N''-fucopentaose I, and sialyllacto-''N''-tetraose a of human milk oligosaccharides as substrate of LnbX in the GH136. In addition, LnbX liberates Galβ1-3GalNAc (GNB) from the sugar chains of globo- and ganglio-series glycosphingolipids <cite>Gotoh2015 | + | This family of glycoside hydrolases contains lacto-''N''-biosidase, as demonstrated for LnbX from ''Bifidobacterium longum'' JCM 1217 <cite>Sakurama2013</cite>. LnbX liberates Galβ1-3GlcNAc (lacto-''N''-biose I, LNB) and lactose from lacto-''N''-tetraose, the main component of human milk oligosaccharides. It hydrolyzed the linkage GlcNAcβ1-3Gal in lacto-''N''-hexaose, lacto-''N''-fucopentaose I, and sialyllacto-''N''-tetraose a of human milk oligosaccharides as substrate of LnbX in the GH136. In addition, LnbX liberates Galβ1-3GalNAc (GNB) from the sugar chains of globo- and ganglio-series glycosphingolipids <cite>Gotoh2015</cite>. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Majority of GH136 lacto-''N''-biosidases require a neighboring chaperon gene for folding. Rarely, chaperone-like gene is fused to lacto-''N''-biosidase gene in case of ErLnb136<sub>I</sub> and ErLnb136<sub>II</sub> from ''Eubacterium ramulus'' <cite>Michael2020</cite>. | ||
== Kinetics and Mechanism == | == Kinetics and Mechanism == | ||
| − | + | GH136 lacto-''N''-biosidases hydrolyze the glycosidic linkage via anomer-retaining mechanism. The acid/base catalytic residue of LnbX (Asp411) formed a water-mediated hydrogen bond with the O1 atom of GlcNAc at subsite -1, and a mechanism of Grotthuss proton transfer was proposed <cite>chihaya2017</cite>. However, subsequent crystallographic reports on three GH136 lacto-''N''-biosidases ("Er"Lnb136, BsaX, and TnX) revealed a direct hydrogen bond between the acid/base catalyst and the O1 atom. This observation suggests that a direct proton transfer mechanism is prevalent within this family <cite>Michael2020 Yamada2022</cite>. | |
== Catalytic Residues == | == Catalytic Residues == | ||
| − | + | For LnbX, the nucleophile and the catalytic acid/base are Asp418 and Asp411, respectively. | |
== Three-dimensional structures == | == Three-dimensional structures == | ||
| Line 44: | Line 43: | ||
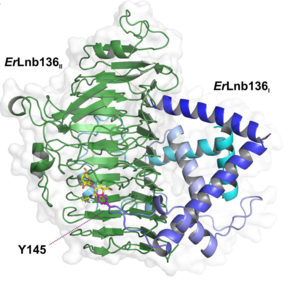
[[file:ErGH136.png|thumb|300px|right|'''Figure 2: '''Overall structure of ''Er''Lnb136 with LNB (yellow), consisting of an N-terminal domain designated as ''Er''Lnb136<sub>I</sub> (cyan-blue) and a C-terminal β-helix domain (green) -''Er''Lnb136<sub>II</sub>.]] | [[file:ErGH136.png|thumb|300px|right|'''Figure 2: '''Overall structure of ''Er''Lnb136 with LNB (yellow), consisting of an N-terminal domain designated as ''Er''Lnb136<sub>I</sub> (cyan-blue) and a C-terminal β-helix domain (green) -''Er''Lnb136<sub>II</sub>.]] | ||
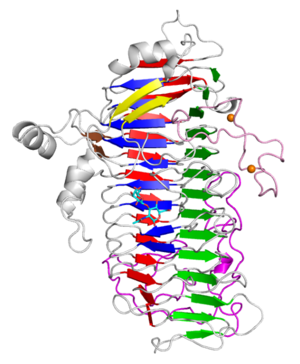
| − | The X-ray crystal structure of the catalytic domain, LnbXc(31-625) revealed a right-handed β helix fold that is usually shared by polysaccharide active enzymes. Three forms, ligand free at 2.36 Å resolution (PDB ID 5GQC), LNB complex at 1.82 Å (PDB ID 5GQF), and GNB complex at 2.70 Å (PDB ID 5GQG) were determined <cite>chihaya2017</cite>. | + | The X-ray crystal structure of the catalytic domain, LnbXc(31-625) revealed a right-handed β helix fold that is usually shared by polysaccharide-active enzymes. Three forms, ligand free at 2.36 Å resolution (PDB ID 5GQC), LNB complex at 1.82 Å (PDB ID 5GQF), and GNB complex at 2.70 Å (PDB ID 5GQG) were determined <cite>chihaya2017</cite>. |
| − | The X-ray crystal structure of'' Er''GH136 in complex with LNB (PDB ID 6KQT) revealed the N-terminal domain (''Er''Lnb136I, from AA 7-224) consists of 8 α-helices (α1-α8) | + | The X-ray crystal structure of '' Er''GH136 in complex with LNB (PDB ID 6KQT) revealed the N-terminal domain (''Er''Lnb136I, from AA 7-224) consists of 8 α-helices (α1-α8) and Y145 of the α6-α7 loop positioned near the active site <cite>Michael2020</cite>. The LNB-complexed structures of the catalytic domain of BsaX from ''Bifidobacterium saguini'' and TnX from ''Tyzzerella nexilis'' were also reported <cite>Yamada2022</cite>. |
== Family Firsts == | == Family Firsts == | ||
| − | ;First stereochemistry determination: | + | ;First stereochemistry determination: LnbX from ''Bifidobacterium longum'' <cite>Sakurama2013</cite>. |
| − | ;First catalytic nucleophile identification: | + | ;First catalytic nucleophile identification: LnbX from ''Bifidobacterium longum'' <cite>chihaya2017</cite>. |
| − | ;First general acid/base residue identification: | + | ;First general acid/base residue identification: LnbX from ''Bifidobacterium longum'' <cite>chihaya2017</cite>. |
| − | ;First 3-D structure: | + | ;First 3-D structure: LnbX from ''Bifidobacterium longum'' <cite>chihaya2017</cite>. |
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 59: | Line 58: | ||
#chihaya2017 pmid=28392148 | #chihaya2017 pmid=28392148 | ||
#Michael2020 pmid=32620774 | #Michael2020 pmid=32620774 | ||
| + | #Yamada2020 pmid=35092420 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
[[Category:Glycoside Hydrolase Families|GH136]] | [[Category:Glycoside Hydrolase Families|GH136]] | ||
Revision as of 19:45, 15 June 2023
This page is currently under construction. This means that the Responsible Curator has deemed that the page's content is not quite up to CAZypedia's standards for full public consumption. All information should be considered to be under revision and may be subject to major changes.
| Glycoside Hydrolase Family GH136 | |
| Clan | GH-N |
| Mechanism | retaining |
| Active site residues | Asp |
| CAZy DB link | |
| http://www.cazy.org/GH136.html | |
Substrate specificities
This family of glycoside hydrolases contains lacto-N-biosidase, as demonstrated for LnbX from Bifidobacterium longum JCM 1217 [1]. LnbX liberates Galβ1-3GlcNAc (lacto-N-biose I, LNB) and lactose from lacto-N-tetraose, the main component of human milk oligosaccharides. It hydrolyzed the linkage GlcNAcβ1-3Gal in lacto-N-hexaose, lacto-N-fucopentaose I, and sialyllacto-N-tetraose a of human milk oligosaccharides as substrate of LnbX in the GH136. In addition, LnbX liberates Galβ1-3GalNAc (GNB) from the sugar chains of globo- and ganglio-series glycosphingolipids [2].
Majority of GH136 lacto-N-biosidases require a neighboring chaperon gene for folding. Rarely, chaperone-like gene is fused to lacto-N-biosidase gene in case of ErLnb136I and ErLnb136II from Eubacterium ramulus [3].
Kinetics and Mechanism
GH136 lacto-N-biosidases hydrolyze the glycosidic linkage via anomer-retaining mechanism. The acid/base catalytic residue of LnbX (Asp411) formed a water-mediated hydrogen bond with the O1 atom of GlcNAc at subsite -1, and a mechanism of Grotthuss proton transfer was proposed [4]. However, subsequent crystallographic reports on three GH136 lacto-N-biosidases ("Er"Lnb136, BsaX, and TnX) revealed a direct hydrogen bond between the acid/base catalyst and the O1 atom. This observation suggests that a direct proton transfer mechanism is prevalent within this family [3, 5].
Catalytic Residues
For LnbX, the nucleophile and the catalytic acid/base are Asp418 and Asp411, respectively.
Three-dimensional structures
The X-ray crystal structure of the catalytic domain, LnbXc(31-625) revealed a right-handed β helix fold that is usually shared by polysaccharide-active enzymes. Three forms, ligand free at 2.36 Å resolution (PDB ID 5GQC), LNB complex at 1.82 Å (PDB ID 5GQF), and GNB complex at 2.70 Å (PDB ID 5GQG) were determined [4]. The X-ray crystal structure of ErGH136 in complex with LNB (PDB ID 6KQT) revealed the N-terminal domain (ErLnb136I, from AA 7-224) consists of 8 α-helices (α1-α8) and Y145 of the α6-α7 loop positioned near the active site [3]. The LNB-complexed structures of the catalytic domain of BsaX from Bifidobacterium saguini and TnX from Tyzzerella nexilis were also reported [5].
Family Firsts
- First stereochemistry determination
- LnbX from Bifidobacterium longum [1].
- First catalytic nucleophile identification
- LnbX from Bifidobacterium longum [4].
- First general acid/base residue identification
- LnbX from Bifidobacterium longum [4].
- First 3-D structure
- LnbX from Bifidobacterium longum [4].
References
- Sakurama H, Kiyohara M, Wada J, Honda Y, Yamaguchi M, Fukiya S, Yokota A, Ashida H, Kumagai H, Kitaoka M, Yamamoto K, and Katayama T. (2013). Lacto-N-biosidase encoded by a novel gene of Bifidobacterium longum subspecies longum shows unique substrate specificity and requires a designated chaperone for its active expression. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(35):25194-25206. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M113.484733 |
- Gotoh A, Katoh T, Sugiyama Y, Kurihara S, Honda Y, Sakurama H, Kambe T, Ashida H, Kitaoka M, Yamamoto K, and Katayama T. (2015). Novel substrate specificities of two lacto-N-biosidases towards β-linked galacto-N-biose-containing oligosaccharides of globo H, Gb5, and GA1. Carbohydr Res. 2015;408:18-24. DOI:10.1016/j.carres.2015.03.005 |
- Pichler MJ, Yamada C, Shuoker B, Alvarez-Silva C, Gotoh A, Leth ML, Schoof E, Katoh T, Sakanaka M, Katayama T, Jin C, Karlsson NG, Arumugam M, Fushinobu S, and Abou Hachem M. (2020). Butyrate producing colonic Clostridiales metabolise human milk oligosaccharides and cross feed on mucin via conserved pathways. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3285. DOI:10.1038/s41467-020-17075-x |
- Yamada C, Gotoh A, Sakanaka M, Hattie M, Stubbs KA, Katayama-Ikegami A, Hirose J, Kurihara S, Arakawa T, Kitaoka M, Okuda S, Katayama T, and Fushinobu S. (2017). Molecular Insight into Evolution of Symbiosis between Breast-Fed Infants and a Member of the Human Gut Microbiome Bifidobacterium longum. Cell Chem Biol. 2017;24(4):515-524.e5. DOI:10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.03.012 |
- Yamada C, Katayama T, and Fushinobu S. (2022). Crystal structures of glycoside hydrolase family 136 lacto-N-biosidases from monkey gut- and human adult gut bacteria. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2022;86(4):464-475. DOI:10.1093/bbb/zbac015 |