CAZypedia celebrates the life of Senior Curator Emeritus Harry Gilbert, a true giant in the field, who passed away in September 2025.
CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article. Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Glycoside Hydrolase Family 16
- Author: Jens Eklöf
- Responsible Editor: Harry Brumer
| Glycoside Hydrolase Family 16 | |
| Clan | GH-B |
| Mechanism | retaining |
| Active site residues | known |
| CAZy DB link | |
| http://www.cazy.org/fam/GH16.html | |
Substrate specificities
Family 16 enzymes cleave β-1,4 or β-1,3 glycosidic bonds in various glucans and galactans. Some members of this family operating on xyloglucan have evolved to exhibit predominantly xyloglucan endo-transglycosylase activity [1]. The substrate specificities found in GH16 are: xyloglucan:xyloglucosyltransferases (EC 2.4.1.207), keratan-sulfate endo-1,4-β-galactosidases (EC 3.2.1.103), endo-1,3-β-glucanases (EC 3.2.1.39), endo-1,3(4)-β-glucanases (EC 3.2.1.6), lichenases (EC 3.2.1.73), β-agarases (EC 3.2.1.81), κ-carrageenases (EC 3.2.1.83) and xyloglucanases (EC 3.2.1.151).
Kinetics and Mechanism
Family 16 enzymes are retaining enzymes, as first shown by NMR [2] on an endo-1,3-1,4-β-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase from Bacillus licheniformis.
Catalytic Residues
The nucleophile was first suggested using an epoxyalkyl β-glycoside inhibitor and subsequent peptide identification by ESI-MS and Edman degradation on an endo-1,3-1,4-β-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens [3]. This was subsequently verified by azide resque of the E134A mutant of a Bacillus licheniformis 1,3-1,4-β-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase resulting in an α-glycosyl product from the β-glycosyl substrate [4]. The acid-base was found by making the E138A mutant from the Bacillus licheniformis 1,3-1,4-β-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase and subsequent azide rescue resulting in a β-glycosyl azide product [4].
Three-dimensional structures
Several family 16 three-dimensional structures have been solved of both archeal, bacterial and eukaryotic origin. The first solved 3-D structure was a hybrid protein of lichenase M from Paenibacillus macerans and BglA from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (PDB 1byh) in 1992 [5]. The first eukaryotic 3-D structure was the xyloglucan endo-transglycosylase PttXET16-34 from Populus tremula×tremuloides (PDB 1umz) [6]. The first archeal 3-D structure was a endo-1,3-β-glucanase Lam16 from Pyrococcus furiosus (PDB 2vy0) [7].
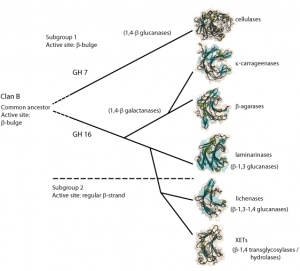
Evolution of GH16
Family 16 is a member of clan GH-B together with family 7 with whom they share their β-jellyroll fold. The different specificities of family 16 has been proposed to have evoloved from an ancestral β-1,3-glucanase [8]. The first branching in family 16 lead to the evolution of the κ-carrageenases and the β-agarases and a later branching event lead to the arisal of the lichenases and the XETs [9] (see figure).
Family firsts
- First stereochemistry determination
- Bacillus licheniformis 1,3-1,4-β-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase by NMR [2].
- First nucleophile identification
- Suggested in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 1,3-1,4-β-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase [3]. Later verified in by azide rescue of inactivated mutants [4].
- First general acid/base residue identification
- Bacillus licheniformis 1,3-1,4-β-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase, first suggested by sequence homology and mutational studies [10]. This was later verified by azide rescue of inactivated mutants [4].
- First 3-D structure
- A hybrid lichenase (Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Paenibacillus macerans) by X-ray crystallography (PDB 1byh) [5].
Reference list
- Baumann MJ, Eklöf JM, Michel G, Kallas AM, Teeri TT, Czjzek M, and Brumer H 3rd. (2007). Structural evidence for the evolution of xyloglucanase activity from xyloglucan endo-transglycosylases: biological implications for cell wall metabolism. Plant Cell. 2007;19(6):1947-63. DOI:10.1105/tpc.107.051391 |
- Malet C, Jiménez-Barbero J, Bernabé M, Brosa C, and Planas A. (1993). Stereochemical course and structure of the products of the enzymic action of endo-1,3-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase from Bacillus licheniformis. Biochem J. 1993;296 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):753-8. DOI:10.1042/bj2960753 |
- Høj PB, Condron R, Traeger JC, McAuliffe JC, and Stone BA. (1992). Identification of glutamic acid 105 at the active site of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 1,3-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase using epoxide-based inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(35):25059-66. | Google Books | Open Library
- Viladot JL, de Ramon E, Durany O, and Planas A. (1998). Probing the mechanism of Bacillus 1,3-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolases by chemical rescue of inactive mutants at catalytically essential residues. Biochemistry. 1998;37(32):11332-42. DOI:10.1021/bi980586q |
- Keitel T, Simon O, Borriss R, and Heinemann U. (1993). Molecular and active-site structure of a Bacillus 1,3-1,4-beta-glucanase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90(11):5287-91. DOI:10.1073/pnas.90.11.5287 |
- Johansson P, Brumer H 3rd, Baumann MJ, Kallas AM, Henriksson H, Denman SE, Teeri TT, and Jones TA. (2004). Crystal structures of a poplar xyloglucan endotransglycosylase reveal details of transglycosylation acceptor binding. Plant Cell. 2004;16(4):874-86. DOI:10.1105/tpc.020065 |
- Ilari A, Fiorillo A, Angelaccio S, Florio R, Chiaraluce R, van der Oost J, and Consalvi V. (2009). Crystal structure of a family 16 endoglucanase from the hyperthermophile Pyrococcus furiosus--structural basis of substrate recognition. FEBS J. 2009;276(4):1048-58. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06848.x |
- Barbeyron T, Gerard A, Potin P, Henrissat B, and Kloareg B. (1998). The kappa-carrageenase of the marine bacterium Cytophaga drobachiensis. Structural and phylogenetic relationships within family-16 glycoside hydrolases. Mol Biol Evol. 1998;15(5):528-37. DOI:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025952 |
- Michel G, Chantalat L, Duee E, Barbeyron T, Henrissat B, Kloareg B, and Dideberg O. (2001). The kappa-carrageenase of P. carrageenovora features a tunnel-shaped active site: a novel insight in the evolution of Clan-B glycoside hydrolases. Structure. 2001;9(6):513-25. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00612-8 |
- Juncosa M, Pons J, Dot T, Querol E, and Planas A. (1994). Identification of active site carboxylic residues in Bacillus licheniformis 1,3-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(20):14530-5. | Google Books | Open Library