CAZypedia needs your help! We have many unassigned GH, PL, CE, AA, GT, and CBM pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute to CAZypedia. Read more here, and in the 10th anniversary article in Glycobiology.
New to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
*
Consider attending the 15th Carbohydrate Bioengineering Meeting in Ghent, 5-8 May 2024.
Difference between revisions of "Carbohydrate Binding Module Family 100"
Harry Brumer (talk | contribs) m |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- RESPONSIBLE CURATORS: Please replace the {{UnderConstruction}} tag below with {{CuratorApproved}} when the page is ready for wider public consumption --> | <!-- RESPONSIBLE CURATORS: Please replace the {{UnderConstruction}} tag below with {{CuratorApproved}} when the page is ready for wider public consumption --> | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{CuratorApproved}} |
* [[Author]]: [[User:Guanchen Liu|Guanchen Liu]] | * [[Author]]: [[User:Guanchen Liu|Guanchen Liu]] | ||
* [[Responsible Curator]]: [[User:Yaoguang Chang|Yaoguang Chang]] | * [[Responsible Curator]]: [[User:Yaoguang Chang|Yaoguang Chang]] | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== Ligand specificities == | == Ligand specificities == | ||
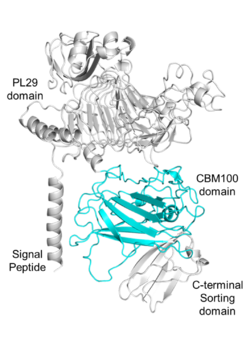
| − | + | [[File:Fig.1 300.png|thumb|250px|right|'''Figure 1. Domain analysis of the parent enzyme of PhCBM100.'''The enzyme consists of a signal peptide (1-23 amino acids), a [[PL29]] domain (68-399 amino acids), a CBM100 domain (viz., PhCBM100; 555-785 amino acids) and a C-terminal sorting domain (786-851 amino acids)<cite>Liu2023</cite>.]] | |
| − | + | The first characterized member of the CBM100 family, PhCBM100<cite>Liu2023</cite>, was found in a [[PL29]] putative chondroitin lyase from ''Polaribacter haliotis''. PhCBM100 bound specifically to chondroitin sulfates (CSs) including CS-A, CS-C and fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from sea cucumber ''Apostichopus japonicus'', whereas it was incapable of binding to other glycosaminoglycans or polyuronic acids. PhCBM100 displays high affinity for CS-A and CS-C with the ''K''<sub>a</sub> values of 2.1×10<sup>6</sup> M<sup>-1</sup> and 6.0×10<sup>6</sup> M<sup>-1</sup>, respectively, as demonstrated by affinity electrophoresis assays <cite>Liu2023</cite>. | |
| − | '' | ||
== Structural Features == | == Structural Features == | ||
| − | + | [[File:Fig.2 300.png|thumb|400px|right|'''Figure 2. Structure of PhCBM100.''' (A) Schematic representation of PhCBM100 showing helices in yellow and strands in cyan. (B) Detailed view of the putative PhCBM100 binding site. The surface is colored by electrostatic potential, from blue (positive charge) to red (negative charge) <cite>Liu2023</cite>.]] | |
| − | + | The 1.55 Å resolution X-ray crystal structure of PhCBM100 ([{{PDBlink}}8jiy PDB 8jiy]) exhibited a β-sandwich fold formed of 10 β-strands and 2 helices<cite>Liu2023</cite>. | |
| − | + | A groove with both a distinct overall positive charge and a high degree of conserved residues is proposed as the binding site, it is enriched with hydrophilic amino acids. As the result of molecular docking, the basic amino acid residues (e.g., Lys-40, Arg-122 and Arg-201) of PhCBM100 may contribute to CS binding through ionic contacts<cite>Liu2023</cite>. | |
| − | |||
== Functionalities == | == Functionalities == | ||
| − | + | PhCBM100 is a component of a [[PL29]] enzyme that displays chondroitin-sulfate ABC endolyase activity, consistent with the PhCBM100 specificity. The ''in situ'' visualization of chondroitin sulfate in animal tissues (e.g., chicken cartilage, bovine muscle, and porcine laryngeal cartilage) was realized by utilizing a fluorescent probe constructed by fusing PhCBM100 with a green fluorescent protein<cite>Liu2023</cite>. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Family Firsts == | == Family Firsts == | ||
| − | ;First Identified | + | ;First Identified: The chondroitin sulfate binding PhCBM100 from the ''P. haliotis'' [[PL29]] putative chondroitin lyase was the first member of the family to be identified and characterized<cite>Liu2023</cite>. |
| − | : | + | ;First Structural Characterization: PhCBM100 was the first structurally characterized CBM100<cite>Liu2023</cite>. |
| − | ;First Structural Characterization | ||
| − | : | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
| − | # | + | #Liu2023 pmid=37951443 |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
<!-- Do not delete this Category tag --> | <!-- Do not delete this Category tag --> | ||
[[Category:Carbohydrate Binding Module Families|CBM100]] | [[Category:Carbohydrate Binding Module Families|CBM100]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:40, 16 February 2024
This page has been approved by the Responsible Curator as essentially complete. CAZypedia is a living document, so further improvement of this page is still possible. If you would like to suggest an addition or correction, please contact the page's Responsible Curator directly by e-mail.
| CAZy DB link | |
| http://www.cazy.org/CBM100.html |
Ligand specificities
The first characterized member of the CBM100 family, PhCBM100[1], was found in a PL29 putative chondroitin lyase from Polaribacter haliotis. PhCBM100 bound specifically to chondroitin sulfates (CSs) including CS-A, CS-C and fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus, whereas it was incapable of binding to other glycosaminoglycans or polyuronic acids. PhCBM100 displays high affinity for CS-A and CS-C with the Ka values of 2.1×106 M-1 and 6.0×106 M-1, respectively, as demonstrated by affinity electrophoresis assays [1].
Structural Features
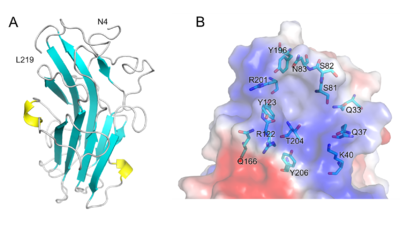
The 1.55 Å resolution X-ray crystal structure of PhCBM100 (PDB 8jiy) exhibited a β-sandwich fold formed of 10 β-strands and 2 helices[1]. A groove with both a distinct overall positive charge and a high degree of conserved residues is proposed as the binding site, it is enriched with hydrophilic amino acids. As the result of molecular docking, the basic amino acid residues (e.g., Lys-40, Arg-122 and Arg-201) of PhCBM100 may contribute to CS binding through ionic contacts[1].
Functionalities
PhCBM100 is a component of a PL29 enzyme that displays chondroitin-sulfate ABC endolyase activity, consistent with the PhCBM100 specificity. The in situ visualization of chondroitin sulfate in animal tissues (e.g., chicken cartilage, bovine muscle, and porcine laryngeal cartilage) was realized by utilizing a fluorescent probe constructed by fusing PhCBM100 with a green fluorescent protein[1].
Family Firsts
- First Identified
- The chondroitin sulfate binding PhCBM100 from the P. haliotis PL29 putative chondroitin lyase was the first member of the family to be identified and characterized[1].
- First Structural Characterization
- PhCBM100 was the first structurally characterized CBM100[1].
References
- Liu G, Chang Y, Mei X, Chen G, Zhang Y, Jiang X, Tao W, and Xue C. (2024). Identification and structural characterization of a novel chondroitin sulfate-specific carbohydrate-binding module: The first member of a new family, CBM100. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;255:127959. DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127959 |