CAZypedia needs your help! We have many unassigned GH, PL, CE, AA, GT, and CBM pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute to CAZypedia. Read more here, and in the 10th anniversary article in Glycobiology.
New to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
*
Consider attending the 15th Carbohydrate Bioengineering Meeting in Ghent, 5-8 May 2024.
Difference between revisions of "Polysaccharide Lyase Family 15"
Emil Stender (talk | contribs) |
Emil Stender (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
== Kinetics and Mechanism == | == Kinetics and Mechanism == | ||
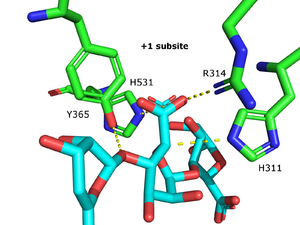
| − | [[Image:Catalytic_PL15.png|thumb|600|'''Figure 1''' +1 subsite of the alginate lyase Atu3025 | + | [[Image:Catalytic_PL15.png|thumb|600|'''Figure 1''' +1 subsite of the alginate lyase Atu3025]] |
The β-elimination catalyzed by the PL15 enzymes results in the formation of a C4-C5 unsaturated sugar at the new non-reducing end. The first step is the neutralization of the acid group in the +1 subsite by the conserved H531 and R314 (Atu3025 numbering)<cite>Ochiai2010</cite>. This lowers the pKa value of the C5-proton allowing for abstraction by the catalytic base (Figure 1). A catalytic acid then donates a proton to the glycosidic linkage resulting in the β-elimination. | The β-elimination catalyzed by the PL15 enzymes results in the formation of a C4-C5 unsaturated sugar at the new non-reducing end. The first step is the neutralization of the acid group in the +1 subsite by the conserved H531 and R314 (Atu3025 numbering)<cite>Ochiai2010</cite>. This lowers the pKa value of the C5-proton allowing for abstraction by the catalytic base (Figure 1). A catalytic acid then donates a proton to the glycosidic linkage resulting in the β-elimination. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
== Three-dimensional structures == | == Three-dimensional structures == | ||
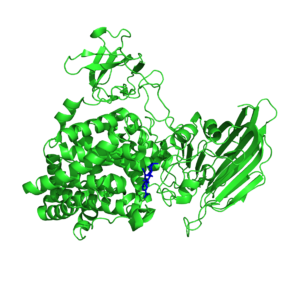
| − | + | [[Image:Atu3025_structure.png|thumb|1000|'''Figure 2''' Crystal structures of the substrate complex of the monomeric Atu3025 (PDB: 3AFL) with the substrate in blue.]] | |
| + | There is only a single crystal structure available in PL15. That of the alginate lyase Atu3025 from ''Agrobacterium fabrum'' (Figure 2) <cite>Ochiai2010</cite>. The catalytic domains consists of an N-terminal (α/α)6 barrel domain and a C-terminal anti-parallel β-sheet domain. The catalytic site is located between the two domains with the catalytic residues and the arginine charge neutralizer located in the (α/α)<sub>6</sub> barrel and the histidine neutralizer in a loop extending into the active site from the anti-parallel β-sheet domain <cite>Ochiai2010</cite>. | ||
== Family Firsts == | == Family Firsts == | ||
| − | ;First | + | ;First catalytic activity: Alginate lyase IV from ''Sphingomonas sp'' <cite>Miyake2003</cite>. |
| − | ;First catalytic | + | ;First catalytic base/acid: Atu3025 from ''Agrobacterium fabrum'' <cite>Ochiai2010</cite>. |
| − | ;First | + | ;First charge neutralizer: Atu3025 from ''Agrobacterium fabrum'' <cite>Ochiai2010</cite>. |
| − | ;First 3-D structure: | + | ;First 3-D structure: Atu3025 from ''Agrobacterium fabrum'' <cite>Ochiai2010</cite>. |
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 63: | Line 64: | ||
#Haug1966 Haug, A., Larsen, B., and Smidsrod, O. (1966) A study of constitution of alginic acid by partial acid hydrolysis. Acta Chem. Scand. 20, 183–190 | #Haug1966 Haug, A., Larsen, B., and Smidsrod, O. (1966) A study of constitution of alginic acid by partial acid hydrolysis. Acta Chem. Scand. 20, 183–190 | ||
#Garron2010 pmid=20805221 | #Garron2010 pmid=20805221 | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Polysaccharide Lyase Families|PL015]] | [[Category:Polysaccharide Lyase Families|PL015]] | ||
Revision as of 05:28, 3 July 2019
This page is currently under construction. This means that the Responsible Curator has deemed that the page's content is not quite up to CAZypedia's standards for full public consumption. All information should be considered to be under revision and may be subject to major changes.
- Author: ^^^Emil Stender^^^
- Responsible Curator: ^^^Birte Svensson^^^
| Polysaccharide Lyase Family 15 | |
| 3D structure | (α/α)6 barrel + anti-parallel β-sheet |
| Mechanism | β-elimination |
| Charge neutralizer | Arginine and histidine |
| Active site residues | known |
| CAZy DB link | |
| http://www.cazy.org/PL15.html | |
Substrate specificities
PL15 currently contains 2 subfamilies [1] as well as several proteins currently not assigned to any subfamily. Subfamily one has been shown to only degrade alginate [2, 3, 4, 5] while subfamily 2 has been found to be heparin and heparan sulfate lyases [6, 7]. Alginate consisting of 1,4 linked β-D-mannuronic acid and α-L-guluronic acid arranged in poly-mannuronic acid blocks, poly-guluronic acid blocks or poly-mannuronic/guluronic acid blocks [8, 9]. Heparin consisting of disaccharide repeating units of which the most common is 2-O-sulfated 1,4 linked α-L-iduronic acid and 6-O-sulfated, N-sulfated glucosamine [IdoA(2S)-GlcNS(6S)]. Heparan sulfate being very similar to heparin having the IdoA replaced with β-D-glucuronic acid with a considerably more variable sulfation and acetylation pattern [10].
Kinetics and Mechanism
The β-elimination catalyzed by the PL15 enzymes results in the formation of a C4-C5 unsaturated sugar at the new non-reducing end. The first step is the neutralization of the acid group in the +1 subsite by the conserved H531 and R314 (Atu3025 numbering)[3]. This lowers the pKa value of the C5-proton allowing for abstraction by the catalytic base (Figure 1). A catalytic acid then donates a proton to the glycosidic linkage resulting in the β-elimination.
Catalytic Residues
After charge neutralization a histidine functions as the catalytic base and a tyrosine the acid. They were originally identified as H311 and Y365 in Atu3025 from Agrobacterium fabrum [3].
Three-dimensional structures
There is only a single crystal structure available in PL15. That of the alginate lyase Atu3025 from Agrobacterium fabrum (Figure 2) [3]. The catalytic domains consists of an N-terminal (α/α)6 barrel domain and a C-terminal anti-parallel β-sheet domain. The catalytic site is located between the two domains with the catalytic residues and the arginine charge neutralizer located in the (α/α)6 barrel and the histidine neutralizer in a loop extending into the active site from the anti-parallel β-sheet domain [3].
Family Firsts
- First catalytic activity
- Alginate lyase IV from Sphingomonas sp [2].
- First catalytic base/acid
- Atu3025 from Agrobacterium fabrum [3].
- First charge neutralizer
- Atu3025 from Agrobacterium fabrum [3].
- First 3-D structure
- Atu3025 from Agrobacterium fabrum [3].
References
<biblio>
- Lombard2010 pmid=20925655
- Miyake2003 pmid=12729723
- Ochiai2010 pmid=20507980
- Jagtap2014 pmid=24795372
- Hashimoto20005 pmid=16233753
- Cartmell2017 pmid=28630303
- Helbert2019 pmid=30850540
- Haug1967 Haug, A., Larsen, B., and Smidsrod, O. (1967) Studies on sequence of uronic acid residues in alginic acid. Acta Chem. Scand. 21, 691–704
- Haug1966 Haug, A., Larsen, B., and Smidsrod, O. (1966) A study of constitution of alginic acid by partial acid hydrolysis. Acta Chem. Scand. 20, 183–190
- Garron2010 pmid=20805221