CAZypedia celebrates the life of Senior Curator Emeritus Harry Gilbert, a true giant in the field, who passed away in September 2025.
CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article. Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Difference between revisions of "Carbohydrate Binding Module Family 16"
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== Ligand specificities == | == Ligand specificities == | ||
Family 16 CBMs ([http://www.cazy.org/CBM16.html CAZy - CBM16]) are found essentially in bacteria (with the exception of some CBM16 members in archaea). They are also found associated with catalytic modules belonging mainly to 4 families of CAZymes: [[GH5]] mannanases <cite>Bae2008 Su2010</cite>, [[GH16]] kappa carrageenases <cite>Barbeyron1998 Matard-Mann2017 Salmean2018</cite>, [[GH18]] chitinases <cite>Barabote2009</cite> and [[PL18]] alginate lyases <cite>Dong2014 Sim2017</cite>. Binding to glucomannan and kappa-carrageenan has been demonstrated <cite>Bae2008 Su2010 Salmean2018</cite>. CBM16 binding to glucomannan (mixed β-1,4-linked polymer contains both glucose and mannose) has been studied by mean of ITC (isothermal titration calorimetry) analysis and X-ray crystallography of complexes with pentomannan and pentoglucan <cite>Bae2008 Su2010</cite>. Conversely, binding to kappa-carrageenan has been shown by a double-blind approach using polysaccharide microarrays <cite>Salmean2018</cite>. | Family 16 CBMs ([http://www.cazy.org/CBM16.html CAZy - CBM16]) are found essentially in bacteria (with the exception of some CBM16 members in archaea). They are also found associated with catalytic modules belonging mainly to 4 families of CAZymes: [[GH5]] mannanases <cite>Bae2008 Su2010</cite>, [[GH16]] kappa carrageenases <cite>Barbeyron1998 Matard-Mann2017 Salmean2018</cite>, [[GH18]] chitinases <cite>Barabote2009</cite> and [[PL18]] alginate lyases <cite>Dong2014 Sim2017</cite>. Binding to glucomannan and kappa-carrageenan has been demonstrated <cite>Bae2008 Su2010 Salmean2018</cite>. CBM16 binding to glucomannan (mixed β-1,4-linked polymer contains both glucose and mannose) has been studied by mean of ITC (isothermal titration calorimetry) analysis and X-ray crystallography of complexes with pentomannan and pentoglucan <cite>Bae2008 Su2010</cite>. Conversely, binding to kappa-carrageenan has been shown by a double-blind approach using polysaccharide microarrays <cite>Salmean2018</cite>. | ||
| − | |||
== Structural Features == | == Structural Features == | ||
| Line 34: | Line 33: | ||
Even if frequently found within the gene coding for alginate lyase from family [[PL18]], it is absent in the mature form of the enzyme, and no role in alginate degradation has been found up to now <cite>Sim2017</cite>. A chaperone function of this N-terminal module has been proposed after observation that its deletion hindered the correct folding and activity of the catalytic module <cite>Dong2014</cite>. | Even if frequently found within the gene coding for alginate lyase from family [[PL18]], it is absent in the mature form of the enzyme, and no role in alginate degradation has been found up to now <cite>Sim2017</cite>. A chaperone function of this N-terminal module has been proposed after observation that its deletion hindered the correct folding and activity of the catalytic module <cite>Dong2014</cite>. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Family Firsts == | == Family Firsts == | ||
| Line 58: | Line 52: | ||
#Dong2014 pmid=25210041 | #Dong2014 pmid=25210041 | ||
#Sim2017 pmid=29057942 | #Sim2017 pmid=29057942 | ||
| − | |||
#Sunna2001 pmid=11389686 | #Sunna2001 pmid=11389686 | ||
#Cann1999 pmid=10049399 | #Cann1999 pmid=10049399 | ||
Revision as of 10:26, 8 February 2019
This page is currently under construction. This means that the Responsible Curator has deemed that the page's content is not quite up to CAZypedia's standards for full public consumption. All information should be considered to be under revision and may be subject to major changes.
- Author: Maria Matard-Mann
- Responsible Curator: ^^^Elizabeth Ficko-Blean^^^
| CAZy DB link | |
| https://www.cazy.org/CBM16.html |
Ligand specificities
Family 16 CBMs (CAZy - CBM16) are found essentially in bacteria (with the exception of some CBM16 members in archaea). They are also found associated with catalytic modules belonging mainly to 4 families of CAZymes: GH5 mannanases [1, 2], GH16 kappa carrageenases [3, 4, 5], GH18 chitinases [6] and PL18 alginate lyases [7, 8]. Binding to glucomannan and kappa-carrageenan has been demonstrated [1, 2, 5]. CBM16 binding to glucomannan (mixed β-1,4-linked polymer contains both glucose and mannose) has been studied by mean of ITC (isothermal titration calorimetry) analysis and X-ray crystallography of complexes with pentomannan and pentoglucan [1, 2]. Conversely, binding to kappa-carrageenan has been shown by a double-blind approach using polysaccharide microarrays [5].
Structural Features
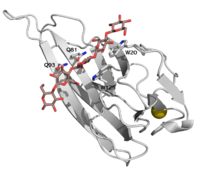
CBM16 is a type B CBM family, with a characteristic concave cleft, allowing the binding of substrate longer than triose. The ligand binding cleft shows some promiscuity as it can accommodate both pentoses (containing glucose and mannose), but only in the context of planar polymer like β-1,4-glucans, and not helical β-1,3-glucans [1]. The crystallographic structure determination of both CBMs from Caldanaerobius polysaccharolyticus (formerly Thermoanaerobacterium polysaccharolyticum) ManA revealed the importance of two aromatic residues in the binding cleft, as long as two stretches of polar residues on both sides of the cleft [1]. Affinity studies of targeted mutants for the predicted key resides confirmed the importance of two tryptophans (Trp-20 and Trp-125), and two glutamines (Gln-81 and Gln-93) [2].
Based on sequence similarity and conservation of secondary structure elements it has been proposed that, along with the CBM4, CBM17, CBM22 and CBM27 families, they form a superfamily [9].
Functionalities
In the Man5A of Caldanaerobius polysaccharolyticus, the deletion of both its CBM16s severely impairs the ability of the catalytic module (GH5) to bind cellulose [10].
In the case of CgkA from Zobellia galactanivorans, the presence of the CBM16 is not required for the enzymatic activity on kappa-carrageenan, but has been shown to take part in the processive mechanism of the catalytic module (GH16) [4].
Even if frequently found within the gene coding for alginate lyase from family PL18, it is absent in the mature form of the enzyme, and no role in alginate degradation has been found up to now [8]. A chaperone function of this N-terminal module has been proposed after observation that its deletion hindered the correct folding and activity of the catalytic module [7].
Family Firsts
- First Identified
Cloning of Man5A GH5 by Cann et al. in 1999 reaveled the presence of two CBM16 tandem associated in C-terminal side. Their deletion resulted in failure of the catalytic module to bind to cellulose column, and significant loss of both mannanase and carboxy methylcellulase activities [10].
- First Structural Characterization
Bae et al. solved the first structures of CBM16 family: both modules of Caldanaerobius polysaccharolyticus Man5A, (PDBID: 2zew, 2zez), and two complexes of CBM16-1, one with cellopentaose (PDBID: 2zex) and one with mannopentaose (PDBID: 2zey)[1].
References
Error fetching PMID 20739280:
Error fetching PMID 29030427:
Error fetching PMID 29410423:
Error fetching PMID 19270083:
Error fetching PMID 25210041:
Error fetching PMID 29057942:
Error fetching PMID 11389686:
Error fetching PMID 10049399:
- Error fetching PMID 18025086:
- Error fetching PMID 20739280:
- Barbeyron T, Gerard A, Potin P, Henrissat B, and Kloareg B. (1998). The kappa-carrageenase of the marine bacterium Cytophaga drobachiensis. Structural and phylogenetic relationships within family-16 glycoside hydrolases. Mol Biol Evol. 1998;15(5):528-37. DOI:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025952 |
- Error fetching PMID 29030427:
- Error fetching PMID 29410423:
- Error fetching PMID 19270083:
- Error fetching PMID 25210041:
- Error fetching PMID 29057942:
- Error fetching PMID 11389686:
- Error fetching PMID 10049399: