CAZypedia celebrates the life of Senior Curator Emeritus Harry Gilbert, a true giant in the field, who passed away in September 2025.
CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article. Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Polysaccharide Lyase Family 17
This page is currently under construction. This means that the Responsible Curator has deemed that the page's content is not quite up to CAZypedia's standards for full public consumption. All information should be considered to be under revision and may be subject to major changes.
- Author: ^^^Emil Stender^^^
- Responsible Curator: ^^^Birte Svensson^^^
| Polysaccharide Lyase Family 17 | |
| 3D structure | (α/α)6 barrel + anti-parallel β-sheet |
| Mechanism | β-eliminationg |
| Charge neutralizer | Asparagine and histidine |
| Active site residues | known |
| CAZy DB link | |
| https://www.cazy.org/PL17.html | |
Substrate specificities
PL17 currently contains 2 subfamilies [1] as well as several proteins currently not assigned to any subfamily. Subfamily 2 has been shown to be exolytic alginate lyases [2, 3, 4, 5] with activity for all tree block structures observed [6]. Alginate consisting of 1,4 linked β-D-mannuronic acid and α-L-guluronic acid arranged in poly-mannuronic acid blocks, poly-guluronic acid blocks or poly-mannuronic/guluronic acid blocks [7, 8]. Subfamily 1 has been found to be hyaluroran endo-lyases or poly-glucuronic acid lyases [6]. Hyaluronan consisting of N-acetyl-D-glucoamine and 1,4 linked D-glucoronic acid [9].
Kinetics and Mechanism
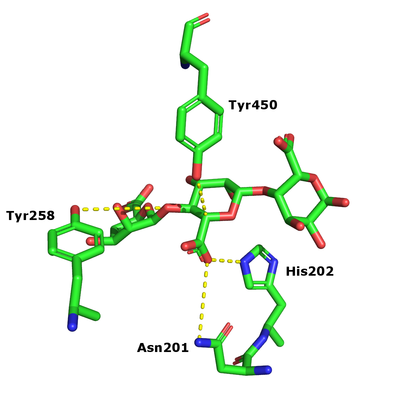
The β-elimination catalyzed by the PL17 enzymes results in the formation of a C4-C5 unsaturated sugar at the new non-reducing end. The first step is the neutralization of the acid group in the +1 subsite by the conserved histidine and asparagine. This lowers the pKa value of the C5-proton allowing for abstraction by the catalytic base (Figure 1). A catalytic acid then donates a proton to the glycosidic linkage resulting in the β-elimination [3].
Catalytic Residues
Content is to be added here.
Three-dimensional structures
Content is to be added here.
Family Firsts
- First stereochemistry determination
- Content is to be added here.
- First catalytic nucleophile identification
- Content is to be added here.
- First general acid/base residue identification
- Content is to be added here.
- First 3-D structure
- Content is to be added here.
References
- Jagtap SS, Hehemann JH, Polz MF, Lee JK, and Zhao H. (2014). Comparative biochemical characterization of three exolytic oligoalginate lyases from Vibrio splendidus reveals complementary substrate scope, temperature, and pH adaptations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014;80(14):4207-14. DOI:10.1128/AEM.01285-14 |
- Park D, Jagtap S, and Nair SK. (2014). Structure of a PL17 family alginate lyase demonstrates functional similarities among exotype depolymerases. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(12):8645-55. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M113.531111 |
-
Shin, J. W., Lee, O. K., Park, H. H., Kim, H. S., and Lee, E. Y. (2015) Molecular characterization of a novel oligoalginate lyase consisting of AlgL- and heparinase II/III-like domains from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia KJ-2 and its application to alginate saccharification. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 32, 917–924
- Wang L, Li S, Yu W, and Gong Q. (2015). Cloning, overexpression and characterization of a new oligoalginate lyase from a marine bacterium, Shewanella sp. Biotechnol Lett. 2015;37(3):665-71. DOI:10.1007/s10529-014-1706-z |
- Mathieu S, Touvrey-Loiodice M, Poulet L, Drouillard S, Vincentelli R, Henrissat B, Skjåk-Bræk G, and Helbert W. (2018). Ancient acquisition of "alginate utilization loci" by human gut microbiota. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):8075. DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-26104-1 |
-
Haug, A., Larsen, B., and Smidsrod, O. (1967) Studies on sequence of uronic acid residues in alginic acid. Acta Chem. Scand. 21, 691–704
-
Haug, A., Larsen, B., and Smidsrod, O. (1966) A study of constitution of alginic acid by partial acid hydrolysis. Acta Chem. Scand. 20, 183–190
- Meyer K, Hobby GL, Chaffee E, and Dawson MH. (1940). THE HYDROLYSIS OF HYALURONIC ACID BY BACTERIAL ENZYMES. J Exp Med. 1940;71(2):137-46. DOI:10.1084/jem.71.2.137 |
- Lombard V, Bernard T, Rancurel C, Brumer H, Coutinho PM, and Henrissat B. (2010). A hierarchical classification of polysaccharide lyases for glycogenomics. Biochem J. 2010;432(3):437-44. DOI:10.1042/BJ20101185 |