CAZypedia needs your help! We have many unassigned GH, PL, CE, AA, GT, and CBM pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute to CAZypedia. Read more here, and in the 10th anniversary article in Glycobiology.
New to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
*
Consider attending the 15th Carbohydrate Bioengineering Meeting in Ghent, 5-8 May 2024.
Difference between revisions of "Anomeric centre (alpha and beta)"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[Image:alpha&beta_arabinose.png|centre]] | [[Image:alpha&beta_arabinose.png|centre]] | ||
| − | |||
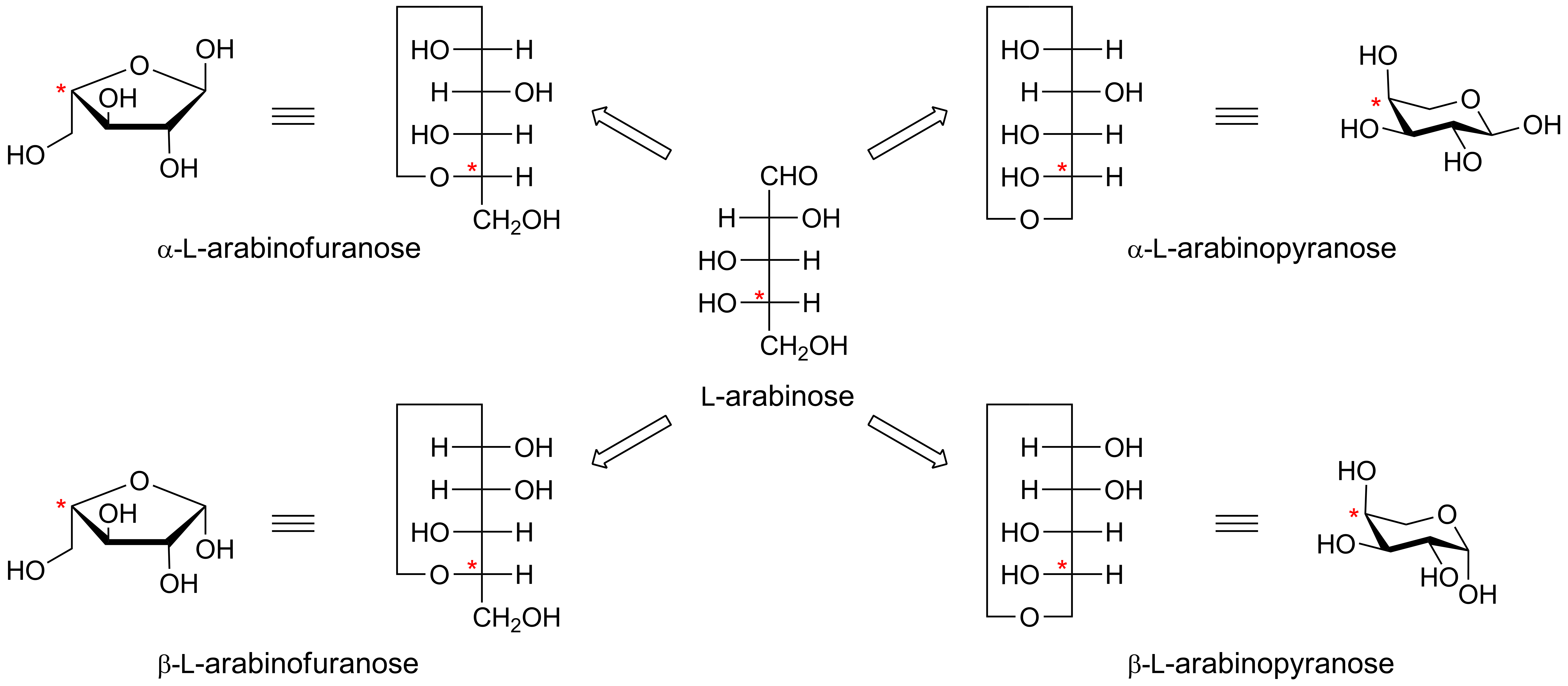
<center>'''Example 1. Fischer projections and Haworth conformational projections of L-arabinose.'''</center> | <center>'''Example 1. Fischer projections and Haworth conformational projections of L-arabinose.'''</center> | ||
[[Image:alpha&beta_fructose.png|centre]] | [[Image:alpha&beta_fructose.png|centre]] | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
[[Image:alpha&beta_glucose.png|centre]] | [[Image:alpha&beta_glucose.png|centre]] | ||
| − | |||
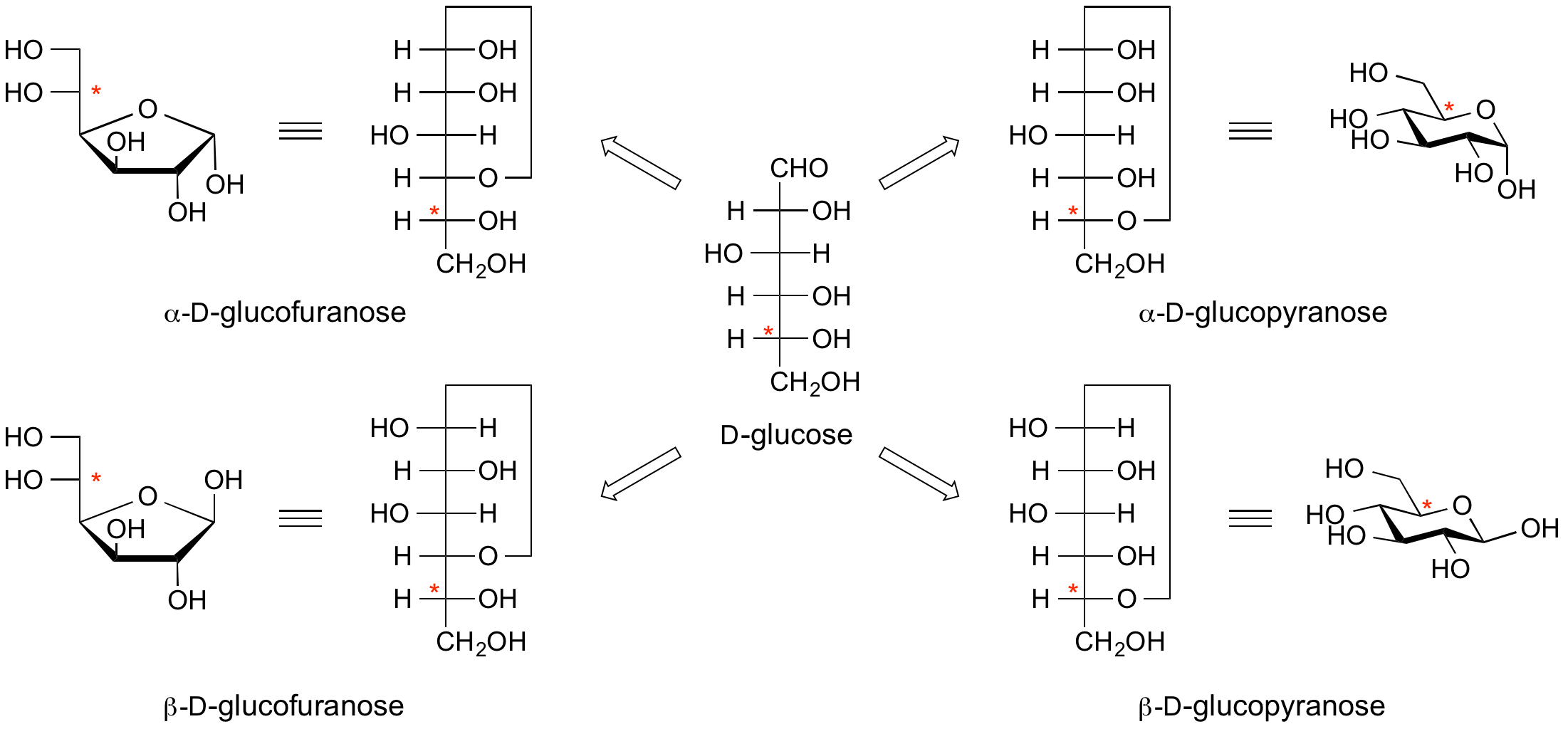
<center>'''Example 3. Fischer projections and Haworth conformational projections of D-glucose.'''</center> | <center>'''Example 3. Fischer projections and Haworth conformational projections of D-glucose.'''</center> | ||
Revision as of 04:25, 23 August 2009
The anomeric centre of a sugar is a stereocentre created from the intramolecular formation of an acetal (or ketal) of a sugar hydroxyl group and an aldehyde (or ketone) group. The two stereoisomers formed from the two possible stereochemistries at the anomeric centre are called anomers. They are diastereoisomers of one another.
The configuration at the anomeric centre (that derived from the carbonyl carbon) is denoted alpha- or beta- by reference to the stereocentre that determines the absolute configuration. In a Fischer projection, if the substituent off the anomeric centre is on the same side as the oxygen of the configurational (D- or L-) carbon, then it is the alpha-anomer. If it is directed in the opposite direction it is the beta-anomer.
In the case of D-hexopyranoses drawn in the 'usual' Haworth projection, the alpha-D-anomer is the isomer with the anomeric substituent on the opposite face to the C5 (hydroxymethyl) substitutent, ie directed ‘down’; the beta-D-anomer is that with the anomeric substituent being on the same face as the C5 hydroxymethyl substitutent, ie directed up. For L-hexoses the alpha-L-anomer has the anomeric group pointing up; the beta-L-anomer has this group pointing down.
References
- Carbohydrates: The essential molecules of life, R.V. Stick, S.J. Williams, Elsevier, 2009, 474 pages.