CAZypedia needs your help! We have many unassigned GH, PL, CE, AA, GT, and CBM pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute to CAZypedia. Read more here, and in the 10th anniversary article in Glycobiology.
New to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
*
Consider attending the 15th Carbohydrate Bioengineering Meeting in Ghent, 5-8 May 2024.
Carbohydrate Binding Module Family 80
This page is currently under construction. This means that the Responsible Curator has deemed that the page's content is not quite up to CAZypedia's standards for full public consumption. All information should be considered to be under revision and may be subject to major changes.
- Author: ^^^Immacolata Venditto^^^
- Responsible Curator: ^^^Harry Gilbert^^^
| CAZy DB link | |
| http://www.cazy.org/CBM80.html |
Ligand specificities
CBM80 is a small bacterial CBM family comprising around 96 amino acids and identified in the Ruminococcus flavefaciens cellulosome [1]. CBM80 displays specificity for β-1,4- and mixed linked β-1,3-1,4-glucans, with some members also binding to β-1,4-mannans [2]. CBM80 is a component of an enzyme that contains catalytic module derived from GH5_4 (CBM80RfGH5-1/2, and CBM80RfGH5) with endo-β1,4-glucanases activity [2]. CBM80 is also component of an enzyme that contains GH5_7 catalytic module with β1,4-mannanase activity [2]. The only family member characterized is CBM80RfGH5-1/2 and the dual specificity of this CBM is consistent with the catalytic modules of the enzymes that hydrolyze β-glucans (GH5_4) or β-mannans (GH5_7) [2]. CBM80RfGH5-1/2 binds galactomannan in addition to the β-glucans with affinities in the range of 104 to 105 M-1, additionally, this CBM binds mannotetraose and not cellotetraose [2].
Structural Features
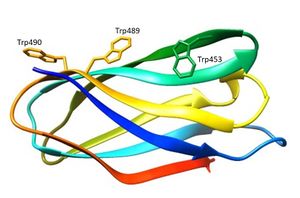
The three-dimensional structure of CBM80RfGH5-1/2 (5fu3) was solved using single-wavelength anomalous diffraction (SAD) methods and selenomethionyl labelled protein [2]. The structure of CBM80RfGH5-1/2 (Figure 1) apo, and in complex with mannohexaose and cellohexaose, was solved with resolutions of 1.0 Å, 1.4 Å and 1.5 Å, respectively [2]. CBM80RfGH5-1/2 has a β-sandwich fold consisting of two β-sheets comprising four (β-sheet 1) and four (β-sheet 2) anti-parallel β-strands, respectively (Figure 1) [2]. The β-sheet 2 of CBM80RfGH-5-1/2 presents a planar hydrophobic surface with a parallel orientation of Trp453 and Trp489 and a perpendicular orientation of a third aromatic residue, Trp490 [2]. The mannohexaose CBM80RfGH5-1/2 complex revealed electron density for mannohexaose along the hydrophobic surface of β-sheet 2 [2]. The structure of CBM80RfGH5-1/2 in complex with cellohexaose revealed electron density for only three glucose units [2].
Functionalities
CBM80, component of enzyme that contains GH5_7 and GH5_4 catalytic modules, binds β-glucans and β-mannans [2]. Other examples of CBMs that recognize both β-1,4-glucans and β-1,4-mannans are found in families CBM16 [3] and CBM29 [4]. The key residues implicated in ligand binding were identified by site-direct mutagenesis. Alanine substitution of Trp453 and Trp489 revealed a complete abrogation of binding to β-glucans and β-mannans, showing the importance of tryptophan residues in ligand recognition [2]. CBMs that bind to β-1,4-glycans typically contain three aromatic residues that make apolar interactions with sugars [4]. The predicted polar interactions between the protein and β-glycans have very little influence on affinity [2].
Family Firsts
- First Identified
- CBM80RfGH5-1/2 from Ruminococcus flavefaciens [2].
- First Structural Characterization
- The first 3D crystal structure solved was CBM80RfGH5-1/2 [2].
References
Error fetching PMID 27298375:
Error fetching PMID 18025086:
Error fetching PMID 12391332:
- Error fetching PMID 20814577:
- Error fetching PMID 27298375:
- Error fetching PMID 18025086:
- Error fetching PMID 12391332: