CAZypedia needs your help! We have many unassigned GH, PL, CE, AA, GT, and CBM pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute to CAZypedia. Read more here, and in the 10th anniversary article in Glycobiology.
New to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
*
Consider attending the 15th Carbohydrate Bioengineering Meeting in Ghent, 5-8 May 2024.
Difference between revisions of "Syn/anti lateral protonation"
Harry Brumer (talk | contribs) (→Table) |
Harry Brumer (talk | contribs) (→Table: added n.c. links) |
||
| Line 1,388: | Line 1,388: | ||
| <cite>Barbirz2008</cite> | | <cite>Barbirz2008</cite> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | * n.c.: [http://www.cazy.org/GH0.html non-classified sequences in the CAZy Database] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 08:59, 8 January 2018
This page has been approved by the Responsible Curator as essentially complete. CAZypedia is a living document, so further improvement of this page is still possible. If you would like to suggest an addition or correction, please contact the page's Responsible Curator directly by e-mail.
- Author: ^^^Wim Nerinckx^^^
- Responsible Curator: ^^^Spencer Williams^^^
Overview
This page provides a table that summarizes the spatial positioning of the catalytic general acid residue in the active sites of glycoside hydrolases, relative to the substrate. The table below updates those found in the seminal paper on this concept by Heightman and Vasella [1], and a following paper by Nerinckx et al. [2].
Background
The "not from above, but from the side" concept of semi-lateral glycosidic oxygen protonation by glycoside hydrolases was introduced by Heightman and Vasella [1]. It was originally only described for beta-equatorial glycoside hydrolases, but appears to be equally applicable to enzymes acting on an alpha-axial glycosidic bond [2]. When dividing subsite -1 into half-spaces by a plane defined by the glycosidic oxygen and C1' and H1' of the –1 glycoside, many ligand-complexed structures reveal that the proton donor is positioned either in the syn half-space (near the ring-oxygen of the –1 glycoside), or in the anti half-space (on the opposite side of the ring-oxygen). Members of the same GH family appear to share a common syn or anti protonator arrangement and further, this specificity appears to be preserved within Clans of families. This page's compilation of subsite -1 occupied complexes shows that about 70% of all GH families are anti protonators.
Closer inspection of crystal structures of –1/+1 subsite-spanning substrates, or substrate-analogue ligands, in complex with enzymes reveals a further intriguing corollary [2, 3]. In substrate-bound complexes with anti protonating GH enzymes, the scissile anomeric bond (often studied using the thio-analogue) shows a dihedral angle φ (O5'-C1'-[O,S]x-Cx) that is in the lowest-energy synclinal (gauche) conformation. The rationale for this is that a minus synclinal dihedral angle φ for an equatorial glycosidic bond, or plus synclinal for an axial glycosidic bond [4], allows for hyperconjugative overlap of the C1'-O5' antibonding orbital with an antiperiplanar-oriented lone pair orbital lobe of the glycosidic oxygen, thereby creating partial double bond character and stabilization of the glycosidic bond by 4–5 kcal/mol; this ground-state stabilizing phenomenon is known as the ‘exo-anomeric effect’ [5, 6, 7]. Anti protonation occurs on the glycosidic oxygen’s antiperiplanar lone pair, thereby removing the stabilizing exo-anomeric effect. This suggests that anti protonation is an enzymic approach for lowering the activation barrier leading to the transition state (Figure 1 centre).
Syn protonating glycoside hydrolases apparently make use of a different approach [2, 3]. In many –1/+1 subsite-spanning ligand complexes, the dihedral angle φ of the scissile anomeric bond has been rotated away from its lowest-energy synclinal position: clockwise to minus-anticlinal or antiperiplanar for beta-equatorial; counterclockwise to plus-anticlinal or antiperiplanar for alpha-axial anomeric bonds. This removes the hyperconjugative overlap and thus also the stabilizing exo-anomeric effect. And because of this rotation, a lone pair of the glycosidic oxygen is directed into the syn half-space, allowing it to be protonated by the syn-positioned proton donor (Figure 1 right).
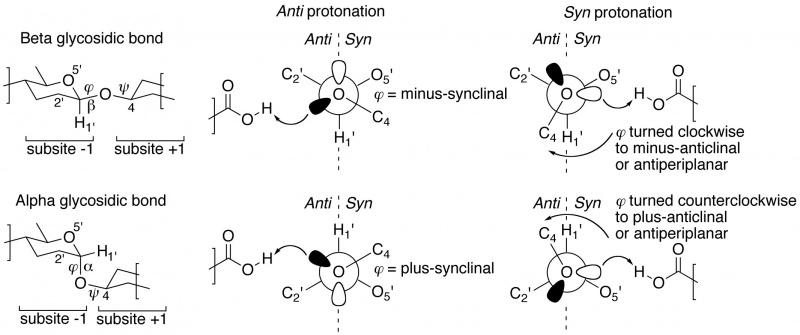
Table of syn/anti protonation examples
This table contains only one example per GH family of a ligand-complexed protein structure where the syn or anti positioning of the proton donor can be clearly observed; other examples may be available on a family-by-family basis. The reader is thus advised to consult the CAZy database for a current, comprehensive list of CAZyme structures. Where available, the selected examples are Michaelis-type complexes with the ligand spanning the -1/+1 subsites, since these have an intact glycosidic or thioglycosidic bond, or are N-analogs of the substrate (e.g. acarbose). In some examples, the proton donor has been mutated (e.g., to the corresponding amide or to an alanine), and in those cases one may wish to look at a superposition of the given PDB example with the structure of the native enzyme. If a Michaelis-type complex is not yet available, the second and third example choices, respectively, are trapped glycosyl-enzyme intermediates and product complexes where subsite -1 is occupied.
Please also be aware that this is a large table with many data. Please contact the page Author or Responsible Curator with corrections.
Table
This table can be re-sorted by clicking on the icons in the header (javascript must be turned on in your browser). To reset the page to be sorted by GH family, click the View tab at the very top of the page.
| Family | Clan | Structure fold | Anomeric specificity | Mechanism | Syn/anti protonator | Example PDB ID | Enzyme | Organism | Ligand | General acid | Nucleophile or General base | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH1 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 2cer | β-glycosidase S | Sulfolobus solfataricus P2 | phenethyl glucoimidazole | Glu206 | Glu387 | [8] |
| GH2 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d / alpha-l | retaining | anti | 2vzu | exo-β-glucosaminidase | Amicolatopsis orientalis | PNP-β-d-glucosamine | Glu469 | Glu541 | [9] |
| GH3 | none | (β/α)8 | beta-d / alpha-l | retaining | anti | 1iex | exo-1,3-1,4-glucanase | Hordeum vulgare | thiocellobiose | Glu491 | Asp285 | [10] |
| GH5 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 1h2j | endo-β-1,4-glucanase | Bacillus agaradhaerens | 2',4'-DNP-2-F-cellobioside | Glu129 | Glu228 | [11] |
| GH6 | none | (β/α)8 | beta-d | inverting | syn | 1qjw | cellobiohydrolase 2 | Hypocrea jecorina | (Glc)2-S-(Glc)2 | Asp221 | debated | [12] |
| GH7 | B | β-jelly roll | beta-d | retaining | syn | 1ovw | endo-1,4-glucanase | Fusarium oxysporum | thio-(Glc)5 | Glu202 | Glu197 | [13] |
| GH8 | M | (α/α)6 | beta-d | inverting | anti | 1kwf | endo-1,4-glucanase | Clostridium thermocellum | cellopentaose | Glu95 | Asp278 | [14] |
| GH9 | none | (α/α)6 | beta-d | inverting | syn | 1rq5 | cellobiohydrolase | Clostridium thermocellum | cellotetraose | Glu795 | Asp383 | [15] |
| GH10 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 2d24 | β-1,4-xylanase | Streptomyces olivaceoviridis E-86 | xylopentaose | Glu128 | Glu236 | [16] |
| GH11 | C | β-jelly roll | beta-d | retaining | syn | 4hk8 | endo-β-1,4-xylanase | Hypocrea jecorina | xylohexaose | Glu177 | Glu86 | [17] |
| GH12 | C | β-jelly roll | beta-d | retaining | syn | 1w2u | endoglucanase | Humicola grisea | thiocellotetraose | Glu205 | Glu120 | [18] |
| GH13 | H | (β/α)8 | alpha-d | retaining | anti | 1cxk | β-cyclodextrin glucanotransferase | Bacillus circulans | maltononaose | Glu257 | Asp229 | [19] |
| GH14 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha-d | inverting | syn | 1itc | β-amylase | Bacillus cereus | maltopentaose | Glu172 | Glu367 | [20] |
| GH15 | L | (α/α)6 | alpha-d | inverting | anti | 1dog | glucoamylase | Aspergillus awamori | 1-deoxynojirimycin | Glu179 | Glu400 | [21] |
| GH16 | B | β-jelly roll | beta-d | retaining | syn | 1urx | β-agarase A | Zobellia galactanivorans | oligoagarose | Glu152 | Glu147 | [22] |
| GH17 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | predicted anti by clan | see e.g. at GH1 | ||||||
| GH18 | K | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 1ffr | chitinase A | Serratia marcescens | (NAG)6 | Glu315 | internal | [23] |
| GH19 | none | lysozyme type | beta-d | inverting | syn | 3wh1 | chitinase | Bryum coronatum | (GlcNAc)4 | Glu61 | Glu70 | [24] |
| GH20 | K | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 1c7s | chitobiase | Serratia marcescens | chitobiose | Glu540 | internal | [25] |
| GH22 | none | lysozyme type | beta-d | retaining | syn | 1h6m | lysozyme C | Gallus gallus | Chit-2-F-chitosyl | Glu35 | Asp52 | [26] |
| GH23 | none | lysozyme type | beta-d | inverting | syn | 1lsp | lysozyme G | Cygnus atratus | Bulgecin A | Glu73 | internal | [27] |
| GH24 | I | α + β | beta-d | inverting | syn | 148l | lysozyme E | Bacteriophage T4 | chitobiosyl | Glu11 | Glu26 | [28] |
| GH26 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 2vx6 | exo-β-mannanase | Cellvibrio japonicus Ueda107 | Gal1Man4 | Glu221 | Glu338 | [29] |
| GH27 | D | (β/α)8 | alpha-d / beta-l | retaining | anti | 3lrm | α-galactosidase | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | raffinose | Asp209 | Asp141 | [30] |
| GH28 | N | β-helix | alpha-d (and α-l-rham) | inverting | anti | 2uvf | exo-polygalacturonosidase | Yersinia enterocolitica ATCC9610D | digalacturonic acid | Asp402 | Asp381 Asp403 | [31] |
| GH29 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha-l | retaining | syn | 3uet | α-1,3/4-fucosidase | Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis | lacto-N-fucopentaose II | Glu217 | Asp172 | [32] |
| GH30 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 2y24 | glucurono-xylanase | Dickea chrysanthemi D1 | glucuronoxylan tetrasaccharide | Glu163 | Glu253 | [33] |
| GH31 | D | (β/α)8 | alpha-d | retaining | anti | 2qmj | maltase-glucoamylase | Homo sapiens | acarbose | Asp542 | Asp443 | [34] |
| GH32 | J | 5-fold β-propeller | beta-d | retaining | anti | 2add | fructan β-(2,1)-fructosidase | Cichorium intybus | sucrose | Glu201 | Asp22 | [35] |
| GH33 | E | 6-fold β-propeller | alpha-d | retaining | anti | 1s0i | transsialidase | Trypanosoma cruzi | sialyllactose | Asp59 | Tyr342 | [36] |
| GH34 | E | 6-fold β-propeller | alpha-d | retaining | anti | 4gzw | N2 neuraminidase | Influenza A Tanzania/205/2010 H3N2 | α-d-Neup5Ac-(2,3)-β-d-Galp-(1,4)-β-d-GlcpNAc | Asp151 | Tyr406 | [37] |
| GH35 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 3ogv | β-galactosidase | Hypocrea jecorina | 2-phenylethyl 1-thio-β-d-galactopyranoside | Glu200 | Glu298 | [38] |
| GH36 | D | (β/α)8 | alpha-d | retaining | anti | 4fns | β-galactosidase | Geobacillus stearothermophilus | 1-deoxy galactonojirimycin | Asp584 | Asp478 | [39] |
| GH37 | G | (α/α)6 | alpha-d | inverting | anti | 2jf4 | trehalase | Escherichia coli | validoxylamine | Asp312 | Glu496 | [40] |
| GH38 | none | (β/α)7 | alpha-d | retaining | anti | 3czn | Golgi α-mannosidase II | Drosophila melanogaster | GlcNAcMan(5)GlcNAc(2) | Asp341 | Asp204 | [41] |
| GH39 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d / alpha-l | retaining | anti | 2bfg | β-xylosidase | Geobacillus stearothermophilus | 2,5-dinitrophenyl-β-d-xyloside | Glu160 | Glu278 | [42] |
| GH42 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d / alpha-l | retaining | anti | 4ucf | β-galactosidase | Bifidobacterium bifidum | d-galactose | Glu161 | Glu320 | [43] |
| GH43 | F | 5-fold β-propeller | beta-d / alpha-l | inverting | anti | 3akh | exo-1,5-α-l-arabinofuranosidase | Streptomyces avermitilis | α-1,5-arabinofuranotriose | Glu196 | Asp220 | [44] |
| GH44 | none | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 2eqd | endoglucanase | Clostridium thermocellum | cellooctaose | Glu186 | Glu359 | [45] |
| GH45 | none | 6-stranded β-barrel | beta-d | inverting | syn | 4eng | endo-1,4-glucanase | Humicola insolens | cellohexaose | Asp121 | Asp10 | [46] |
| GH46 | I | lysozyme type | beta-d | inverting | syn | 4olt | chitosanase | Microbacterium sp. OU01 | hexa-glucosamine | Glu25 | Asp43 | [47] |
| GH47 | none | (α/α)7 | alpha-d | inverting | anti | 1x9d | α-mannosidase I | Homo sapiens | Me-2-S-(α-Man)-2-thio-α-Man | Asp463 | Glu599 | [48], [49] |
| GH48 | M | (α/α)6 | beta-d | inverting | predicted anti by clan | see at GH8 | ||||||
| GH49 | N | β-helix | alpha-d | inverting | predicted anti by clan | see at GH28 | ||||||
| GH50 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 4bq5 | exo-β-agarase | Saccharophagus degradans | neoagarotetraose | Glu535 | Glu695 | [50] |
| GH51 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d / alpha-l | retaining | anti | 1qw9 | α-l-arabinofuranosidase | Geobacillus stearothermophilus | PNP-l-arabinofuranoside | Glu175 | Glu294 | [51] |
| GH52 | O | (α/α)6 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 4c1p | β-xylosidase | Geobacillus thermoglucosidasius | xylobiose | Asp517 | Glu537 | [52] |
| GH53 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 2ccr | β-1,4-galactanase | Bacillus licheniformis | galactotriose | Glu165 | Glu263 | [53] |
| GH54 | none | β-sandwich | beta-d / alpha-l | retaining | anti | 1wd4 | α-l-arabinofuranosidase B | Aspergillus kawachii | l-arabinofuranose | Asp297 | Glu221 | [54] |
| GH55 | none | β-helix | beta-d | inverting | syn | 4tz5 | exo-β-1,3-glucanase | Streptomyces sp. SirexAA-E | laminarihexaose | Glu502 | unknown | [55] |
| GH56 | none | (β/α)7 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 1fcv | hyaluronidase | Apis mellifera | (hyaluron.)4 | Glu113 | internal | [56] |
| GH57 | none | (β/α)7 | alpha-d | retaining | anti | 1k1y | glucanotransferase | Thermococcus litoralis | acarbose | Asp214 | Glu123 | [57] |
| GH59 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 4ccc | β-galactocerebrosidase | Mus musculus | PNP-β-d-galactoside | Glu182 | Glu258 | [58] |
| GH62 | F | 5-fold β-propeller | alpha-l | unknown | predicted anti by clan | see at GH43 | ||||||
| GH63 | G | (α/α)6 | alpha-d | inverting | anti | 5ca3 | α-glucosidase | Escherichia coli | glucose and lactose | Asp501 | Glu727 | [59] |
| GH65 | L | (α/α)6 | alpha-d (and α-l-rham) | inverting | anti | 4ktr | 2-O-α-glucosylglycerol phosphorylase | Bacillus selenitireducens | isofagomine | Glu475 | phosphate | [60] |
| GH66 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha-d | retaining | anti | 5axh | dextranase | Thermoanaerobacter pseudethanolicus | isomaltohexaose | Glu374 | Asp312 | [61] |
| GH67 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha-d | inverting | syn | 1l8n | α-glucuronidase | Geobacillus stearothermophilus | 4-O-methyl-d-glucuronic acid and xylotriose | Glu286 | Asp364 Glu392 | [62] |
| GH68 | J | 5-fold β-propeller | beta-d | retaining | anti | 1pt2 | levansucrase | Bacillus subtilis | sucrose | Glu342 | Asp86 | [63] |
| GH70 | H | (β/α)8 | alpha-d | retaining | anti | 3aic | glucansucrase | Streptococcus mutans | α-acarbose | Glu515 | Asp477 | [64] |
| GH72 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 2w62 | β-1,3-glucanotransferase | Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C | laminaripentaose | Glu176 | Glu275 | [65] |
| GH74 | none | 7-fold β-propeller | beta-d | inverting | syn | 2ebs | cellobiohydrolase (OXG-RCBH) | Geotrichum sp. m128 | xyloglucan heptasaccharide | Asp465 | Asp35 | [66] |
| GH76 | none | (α/α)6 | alpha-d | retaining | anti | 5agd | endo-α-1,6-mannanase | Bacillus circulans | α-1,6-mannopentaose | Asp125 | Asp124 | [67] |
| GH77 | H | (β/α)8 | alpha-d | retaining | anti | 2oww | 4-α-glucanotransferase | Thermus thermofilus | acarbose + 4-deoxy-α-d-glucose | Glu340 | Asp293 | [68] |
| GH78 | H | (α/α)6 | alpha-l | inverting | anti | 3w5n | α-l-rhamnosidase | Streptomyces avermitilis | l-rhamnose | Glu636 | Glu895 | [69] |
| GH79 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 5e9c | heparanase | Homo sapiens | heparin tetrasaccharide | Glu225 | Glu343 | [70] |
| GH80 | I | α + β | beta-d | inverting | predicted syn by clan | see at GH24 | ||||||
| GH81 | none | β-sandwich | beta-d | inverting | syn | 5t4g | endo-β-1,3-glucanase | Bacillus halodurans C-125 | laminarin | Asp466 | Glu542 | [71] |
| GH83 | E | 6-fold β-propeller | alpha-d | retaining | predicted anti by clan | see e.g. at GH33 | ||||||
| GH84 | none | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 2chn | β-N-acetyl-glucosaminidase | Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 | NAG-thiazoline | Glu242 | internal | [72] |
| GH85 | K | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 2w92 | endo-β-N-acetyl-glucosaminidase D | Streptococcus pneumoniae TIGR4 | NAG-thiazoline | Glu337 | internal | [73] |
| GH86 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 4aw7 | β-porphyranase | Bacteroides plebeius | porphyran fragment | Glu152 | Glu279 | [74] |
| GH89 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha-d | retaining | anti | 2vcb | α-N-acetyl-glucosaminidase | Clostridium perfringens | PUGNAc | Glu483 | Glu601 | [75] |
| GH92 | none | (α/α)6 and β-sandw. | alpha-d | inverting | anti | 2ww1 | α-1,2-mannosidase | Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 | thiomannobioside | Glu533 | Asp644 Asp642 | [76] |
| GH93 | E | 6-fold β-propeller | alpha-l | retaining | anti | 3a72 | exo-arabinanase | Penicillium chrysogenum | arabinobiose | Glu246 | Glu174 | [77] |
| GH94 | none | (α/α)6 | beta-d | inverting | syn | 4zli | cellobionic acid phosphorylase | Saccharophagus degradans | 3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-α-d-glucopyranuronic acid | Asp472 | phosphate | [78] |
| GH95 | none | (α/α)6 | alpha-l | inverting | anti | 2ead | α-1,2-l-fucosidase | Bifidobacterium bifidum | Fuc-α-1,2-Gal | Glu566 | Asn423 Asp766 | [79] |
| GH97 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha-d | retaining + inverting | anti | 2zq0 | α-glucosidase | Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 | acarbose | Glu532 | Glu508 | [80] |
| GH98 | none | (β/α)8 and β-sandwich | beta-d | inverting | anti | 2wmg | endo-β-1,4-galactosidase | Streptococcus pneumoniae | A-LewisY pentasaccharide | Glu158 | Asp251 Glu301 | [81] |
| GH99 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha-d | retaining | anti | 4ad4 | endo-α-mannosidase | Bacteroides xylanisolvens | glucose-1,3-isofagomine and α-1,2- mannobiose | Glu336 | debated | [82] |
| GH100 | none | (α/α)6 core | beta-d | inverting | anti | 5gop | invertase | Anabaena (Nostoc) sp. pcc7120 | sucrose | Asp188 | Glu414 | [83] |
| GH102 | none | double-ψ β-barrel | beta-d | retaining | syn | 2pi8 | lytic transglycosylase A | Escherichia coli | chitohexaose | Asp308 | none | [84] |
| GH103 | none | lysozyme type | beta-d | retaining | syn | 1d0k | lytic transglycosylase SLT35 | Escherichia coli | murodipeptides | Glu162 | internal | [85] |
| GH106 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha-l | inverting | anti | 5mwk | α-l-rhamnosidase BT_0986 | Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron | pectin heptasaccharide | Glu461 | Glu593 or Glu561 | [86] |
| GH113 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | anti | 4cd8 | β-mannanase | Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius | mannobioimidazole | Glu151 | Glu231 | [87] |
| GH116 | O | (α/α)6 and β-sandwich | beta-d | retaining | predicted anti by clan | see at GH52 | ||||||
| GH117 | none | 5-fold β-propeller | alpha-l | inverting | anti | 4ak7 | α-1,3-3,6-anhydro-l-galactosidase | Bacteroides plebeius | neoagarobiose | His302 | Asp90 | [88] |
| GH120 | none | parallel β-helix and β-sandwich | beta-d | retaining | anti | 3vsv | β-xylosidase XylC | Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum JW/SL-YS485 | d-xylose | Glu405 | Asp382 | [89] |
| GH123 | none | (β/α)8 and β-sandwich | beta-d | retaining | anti | 5fr0 | exo-β-N-acetyl-galactosaminidase | Clostridium perfringens | N-difluoroacetyl-d-galactosamine | Glu345 | internal | [90] |
| GH125 | L | (α/α)6 | alpha-d | inverting | anti | 5m7y | exo-α-1,6-mannosidase | Clostridium perfringens | 1,6-α-mannotriose | Asp220 | Glu393 | [91] |
| GH127 | none | (α/α)6 and β-sandwich | beta-l | retaining | anti | 3wrg | β-l-arabinofuranosidase | Bifidobacterium longum | l-arabinose | Glu322 | Cys417 | [92] |
| GH128 | A | (β/α)8 | beta-d | retaining | predicted anti by clan | see e.g. at GH1 | ||||||
| GH130 | none | 5-fold β-propeller | beta-d | inverting | anti | 5b0s | β-1,2-mannobiose phosphorylase | Listeria innocua | β-1,2-mannotriose | Asp141 relay | phosphate | [93] |
| GH134 | none | β + α | beta-d | inverting | syn | 5jug | β-mannanase | Streptomyces sp. | mannopentaose | Glu45 | Asp57 | [94] |
| GH137 | none | 5-fold β-propeller | beta-l | unknown | anti | 5mui | β-l-arabinofuranosidase BT_0996 | Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron | pectin oligosaccharide | Glu240 | Glu159 | [86] |
| n.c.* | none | parallel β-helix | alpha-d | inverting | anti | 2vjj | endo-α-N-acetylglucosaminidase | Bacteriophage HK620 | O18A1 O-antigen hexasaccharide | Asp339 | Glu372 | [95] |
References
Error fetching PMID 23137336:
Error fetching PMID 19733839:
Error fetching PMID 26889578:
Error fetching PMID 17002288:
Error fetching PMID 18976664:
Error fetching PMID 12595701:
Error fetching PMID 10508787:
Error fetching PMID 10200171:
Error fetching PMID 21501386:
Error fetching PMID 14756552:
Error fetching PMID 19279191:
Error fetching PMID 24419374:
Error fetching PMID 15364577:
Error fetching PMID 12741813:
Error fetching PMID 8431441:
Error fetching PMID 15062085:
Error fetching PMID 11560481:
Error fetching PMID 10884356:
Error fetching PMID 15299731:
Error fetching PMID 8259514:
Error fetching PMID 18799462:
Error fetching PMID 20592022:
Error fetching PMID 17397864:
Error fetching PMID 22451675:
Error fetching PMID 18036614:
Error fetching PMID 17335500:
Error fetching PMID 23015718:
Error fetching PMID 21130883:
Error fetching PMID 23012371:
Error fetching PMID 17455176:
Error fetching PMID 18599462:
Error fetching PMID 16212978:
Error fetching PMID 27685756:
Error fetching PMID 20739278:
Error fetching PMID 17905739:
Error fetching PMID 15299721:
Error fetching PMID 24766439:
Error fetching PMID 15713668:
Error fetching PMID 18619586:
Error fetching PMID 23921382:
Error fetching PMID 14517232:
Error fetching PMID 24816105:
Error fetching PMID 19089956:
Error fetching PMID 15292273:
Error fetching PMID 25752603:
Error fetching PMID 11080624:
Error fetching PMID 24297913:
Error fetching PMID 27688023:
Error fetching PMID 24828502:
Error fetching PMID 26494689:
Error fetching PMID 14573597:
Error fetching PMID 17498741:
Error fetching PMID 25772148:
Error fetching PMID 17420245:
Error fetching PMID 26575439:
Error fetching PMID 28781080:
Error fetching PMID 19181667:
Error fetching PMID 23150581:
Error fetching PMID 18443291:
Error fetching PMID 20081828:
Error fetching PMID 21543843:
Error fetching PMID 26041776:
Error fetching PMID 17459873:
Error fetching PMID 18981178:
Error fetching PMID 19608744:
Error fetching PMID 10684641:
Error fetching PMID 24582745:
Error fetching PMID 27777307:
Error fetching PMID 24339341:
Error fetching PMID 22393053:
Error fetching PMID 22992047:
Error fetching PMID 27038508:
Error fetching PMID 28026180:
Error fetching PMID 26632508:
Error fetching PMID 18547389:
-
Heightman TD and Vasella AT. Recent Insights into Inhibition, Structure, and Mechanism of Configuration-Retaining Glycosidases. Angew Chem Int Ed. 1999 38(6):750-770. Article online.
- Error fetching PMID 15642336:
- Error fetching PMID 23137336:
-
Pérez S and Marchessault RH. The exo-anomeric effect: experimental evidence from crystal structures. Carbohydr res. 1978 65:114-120. DOI:10.1016/S0008-6215(00)84218-4
-
Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG, and French AD. Exo-anomeric effects on energies and geometries of different conformations of glucose and related systems in the gas phase and aqueous solution. Carbohydr res. 1997 298:1-14. DOI:10.1016/S0008-6215(96)00297-2
- Error fetching PMID 19733839:
- Error fetching PMID 26889578:
- Error fetching PMID 17002288:
- Error fetching PMID 18976664:
- Hrmova M, Varghese JN, De Gori R, Smith BJ, Driguez H, and Fincher GB. (2001). Catalytic mechanisms and reaction intermediates along the hydrolytic pathway of a plant beta-D-glucan glucohydrolase. Structure. 2001;9(11):1005-16. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00673-6 |
- Error fetching PMID 12595701:
- Error fetching PMID 10508787:
- Error fetching PMID 10200171:
- Guérin DM, Lascombe MB, Costabel M, Souchon H, Lamzin V, Béguin P, and Alzari PM. (2002). Atomic (0.94 A) resolution structure of an inverting glycosidase in complex with substrate. J Mol Biol. 2002;316(5):1061-9. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5404 |
- Error fetching PMID 14756552:
- Error fetching PMID 19279191:
- Error fetching PMID 24419374:
- Error fetching PMID 15364577:
- Uitdehaag JC, Mosi R, Kalk KH, van der Veen BA, Dijkhuizen L, Withers SG, and Dijkstra BW. (1999). X-ray structures along the reaction pathway of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase elucidate catalysis in the alpha-amylase family. Nat Struct Biol. 1999;6(5):432-6. DOI:10.1038/8235 |
- Error fetching PMID 12741813:
- Error fetching PMID 8431441:
- Error fetching PMID 15062085:
- Error fetching PMID 11560481:
- Error fetching PMID 24582745:
- Error fetching PMID 10884356:
- Vocadlo DJ, Davies GJ, Laine R, and Withers SG. (2001). Catalysis by hen egg-white lysozyme proceeds via a covalent intermediate. Nature. 2001;412(6849):835-8. DOI:10.1038/35090602 |
- Error fetching PMID 15299731:
- Error fetching PMID 8259514:
- Error fetching PMID 18799462:
- Error fetching PMID 20592022:
- Error fetching PMID 17397864:
- Error fetching PMID 22451675:
- Error fetching PMID 21501386:
- Error fetching PMID 18036614:
- Error fetching PMID 17335500:
- Amaya MF, Watts AG, Damager I, Wehenkel A, Nguyen T, Buschiazzo A, Paris G, Frasch AC, Withers SG, and Alzari PM. (2004). Structural insights into the catalytic mechanism of Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase. Structure. 2004;12(5):775-84. DOI:10.1016/j.str.2004.02.036 |
- Error fetching PMID 23015718:
- Error fetching PMID 21130883:
- Error fetching PMID 23012371:
- Error fetching PMID 17455176:
- Error fetching PMID 18599462:
- Error fetching PMID 16212978:
- Error fetching PMID 27685756:
- Error fetching PMID 20739278:
- Error fetching PMID 17905739:
- Error fetching PMID 15299721:
- Error fetching PMID 24766439:
- Error fetching PMID 15713668:
- Error fetching PMID 18619586:
- Error fetching PMID 23921382:
- Error fetching PMID 14517232:
- Error fetching PMID 24816105:
- Error fetching PMID 19089956:
- Error fetching PMID 15292273:
- Error fetching PMID 25752603:
- Error fetching PMID 11080624:
- Imamura H, Fushinobu S, Yamamoto M, Kumasaka T, Jeon BS, Wakagi T, and Matsuzawa H. (2003). Crystal structures of 4-alpha-glucanotransferase from Thermococcus litoralis and its complex with an inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(21):19378-86. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M213134200 |
- Error fetching PMID 24297913:
- Error fetching PMID 27688023:
- Error fetching PMID 24828502:
- Error fetching PMID 26494689:
- Error fetching PMID 14573597:
- Meng G and Fütterer K. (2003). Structural framework of fructosyl transfer in Bacillus subtilis levansucrase. Nat Struct Biol. 2003;10(11):935-41. DOI:10.1038/nsb974 |
- Ito K, Ito S, Shimamura T, Weyand S, Kawarasaki Y, Misaka T, Abe K, Kobayashi T, Cameron AD, and Iwata S. (2011). Crystal structure of glucansucrase from the dental caries pathogen Streptococcus mutans. J Mol Biol. 2011;408(2):177-86. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.02.028 |
- Hurtado-Guerrero R, Schüttelkopf AW, Mouyna I, Ibrahim AF, Shepherd S, Fontaine T, Latgé JP, and van Aalten DM. (2009). Molecular mechanisms of yeast cell wall glucan remodeling. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(13):8461-9. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M807990200 |
- Error fetching PMID 17498741:
- Error fetching PMID 25772148:
- Error fetching PMID 17420245:
- Fujimoto Z, Jackson A, Michikawa M, Maehara T, Momma M, Henrissat B, Gilbert HJ, and Kaneko S. (2013). The structure of a Streptomyces avermitilis α-L-rhamnosidase reveals a novel carbohydrate-binding module CBM67 within the six-domain arrangement. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(17):12376-85. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M113.460097 |
- Error fetching PMID 26575439:
- Error fetching PMID 28781080:
- Dennis RJ, Taylor EJ, Macauley MS, Stubbs KA, Turkenburg JP, Hart SJ, Black GN, Vocadlo DJ, and Davies GJ. (2006). Structure and mechanism of a bacterial beta-glucosaminidase having O-GlcNAcase activity. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13(4):365-71. DOI:10.1038/nsmb1079 |
- Error fetching PMID 19181667:
- Error fetching PMID 23150581:
- Error fetching PMID 18443291:
- Error fetching PMID 20081828:
- Error fetching PMID 21543843:
- Error fetching PMID 26041776:
- Error fetching PMID 17459873:
- Error fetching PMID 18981178:
- Error fetching PMID 19608744:
- Thompson AJ, Williams RJ, Hakki Z, Alonzi DS, Wennekes T, Gloster TM, Songsrirote K, Thomas-Oates JE, Wrodnigg TM, Spreitz J, Stütz AE, Butters TD, Williams SJ, and Davies GJ. (2012). Structural and mechanistic insight into N-glycan processing by endo-α-mannosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(3):781-6. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1111482109 |
- Error fetching PMID 27777307:
- van Straaten KE, Barends TR, Dijkstra BW, and Thunnissen AM. (2007). Structure of Escherichia coli Lytic transglycosylase MltA with bound chitohexaose: implications for peptidoglycan binding and cleavage. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(29):21197-205. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M701818200 |
- Error fetching PMID 10684641:
- Ndeh D, Rogowski A, Cartmell A, Luis AS, Baslé A, Gray J, Venditto I, Briggs J, Zhang X, Labourel A, Terrapon N, Buffetto F, Nepogodiev S, Xiao Y, Field RA, Zhu Y, O'Neil MA, Urbanowicz BR, York WS, Davies GJ, Abbott DW, Ralet MC, Martens EC, Henrissat B, and Gilbert HJ. (2017). Complex pectin metabolism by gut bacteria reveals novel catalytic functions. Nature. 2017;544(7648):65-70. DOI:10.1038/nature21725 |
- Error fetching PMID 24339341:
- Error fetching PMID 22393053:
- Error fetching PMID 22992047:
- Error fetching PMID 27038508:
- Error fetching PMID 28026180:
-
Huang CH, Zhu Z, Cheng YS, Chan HC, Ko TP, Chen CC, Wang I, Ho MR, Hsu ST, Zeng YF, Huang YN, Liu JR, Guo RT. Structure and Catalytic Mechanism of a Glycoside Hydrolase Family-127 β-L-Arabinofuranosidase (HypBA1). J Bioprocess Biotech. 2014 4:171 DOI:10.4172/2155-9821.1000171
- Error fetching PMID 26632508:
-
Jin Y, Petricevic M, John A, Raich L, Jenkins H, Portela De Souza L, Cuskin F, Gilbert HJ, Rovira C, Goddard-Borger ED, Williams SJ, and Davies GJ. A β-Mannanase with a Lysozyme-like Fold and a Novel Molecular Catalytic Mechanism. ACS Cent Sci. 2016 Nov DOI:10.1021/acscentsci.6b00232
- Error fetching PMID 18547389: